netter25
Cutaneous Receplors: Pacinian Corpuscle
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
Generator poiential
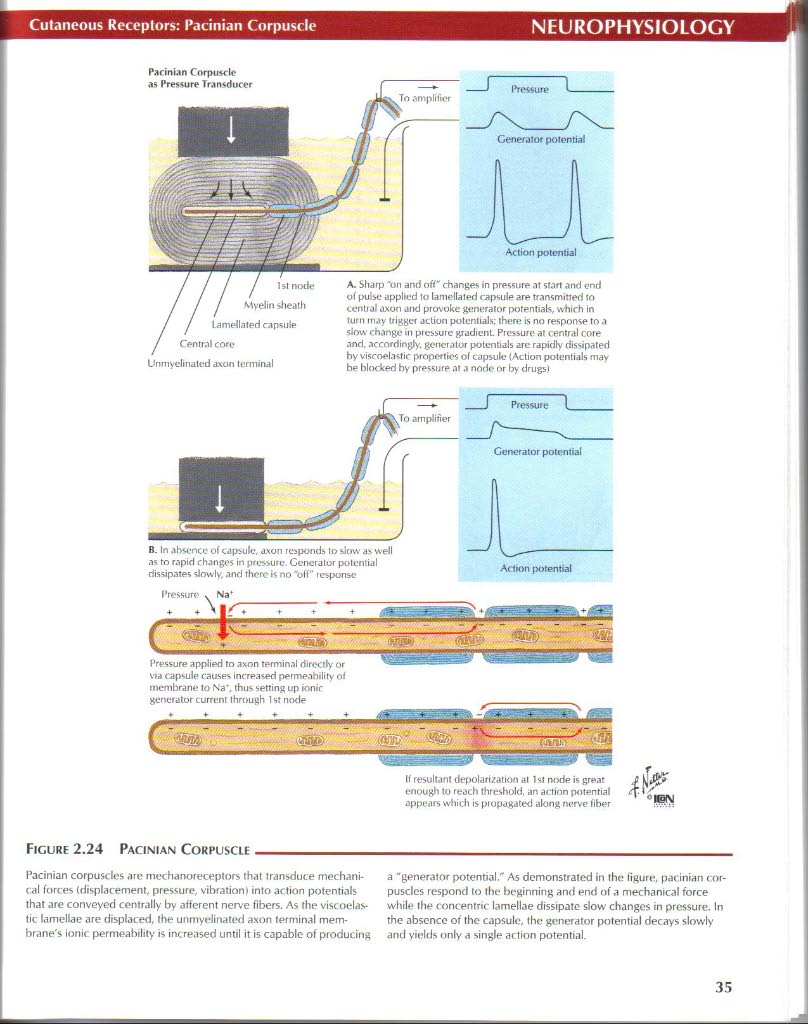
Centr.nl core Unmyclinatcd axon terminal
A. Sliarp 'on and o fi" changes in pressure at start and end of pulse applted to lamellated rapsule are tnnsmitted to central axon and provokc generator potentials,, which in tum may triggcr action potentials; there is no response to a slow change in pressure gradient. Pressure at central core and. accnrdingły. generator potentials arc rapidly dissipated hy viscoelastic pnoperties of capsule (Action potentials may be hlodced by pressure at a nodo or by drugsi
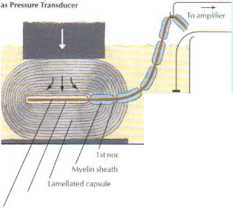
B. In abscncc of capsule, axun responds lo slow as well as to rapid changes in pressure. Generator potential dissipates slowly, and there is no "off" response
Generator potential

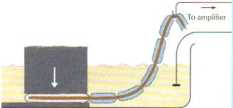
via rapsule causes inrreased permeability of membranę to Na*, thus setting up ionir generator current through 1 st node
C '-m' ~" ~
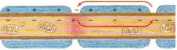
If resultant depolarutation at lst node is great enough to reach threshold, an action potential appears which is propagated along nr*rve fiber

Figurę 2.24 Pacinian Corpuscle_
Pacinian corpuscle* arc mechanoreceptors that transduce mechani-cal forces (displacement, pressure, vibration) into action potentials that are conveyed centrally by afferent nerve fibers. As the viscoelas-tic lamellae are displaced, the unmyelinated axon terminal membranę^ ionic permeability is inereased until it is capablc of producing a "generator potential.' As demonstrated in the llRure, pacinian cor-puscles respond to the boginning and end of a mechankral force while the concentnc lamellae dissipatc slow changes in pressure. In the absence of the capsule, the generator potential decays slowly and yields only a single action potential.
35
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
50914 netter27 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY A(3 fibers from paciniform corpuscles and Rufiini temiinalsPropr
netter39 Custatory (Taste) System: Receptors NEUROPHYSIOLOGY A. Tongue B. Section
netter24 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYCutaneous Sensory Receplors Melanoryte Arrectot muscle ofliair, Sebaceous gl
netter10 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYSynaptic Tr.insmission: Temporal and Spatial Summation C. Icmporal exritator
netter11 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYCerebrospinal Fluid (CSF): Brain Ventricles and CSF Composition Frontal (ant
netter127 Autonomie lnnervationGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY m generał sympathetics decrease peristals
netter149 Pancreas Secretion rates i shown SecretinGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY General
netter2 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Central sulcus (Rotando)Organizalion of Ihe Brain: Cerebrum Postcentral gyru
netter20 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYThe Cerebral Cortex Sm!,} Spn4,,,v Sensory Promotor; orientation, eye and
netter30 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Sensory Pathways: I Spinothałamic iract lower part of medulla
netter36 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Audilory System: Pathways temporal lobe cortex Medial geniculate body High
netter40 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYGustatory (Taste) System: Pathways Sensory cortex łjust below face area) Lat
więcej podobnych podstron