38668 netter157
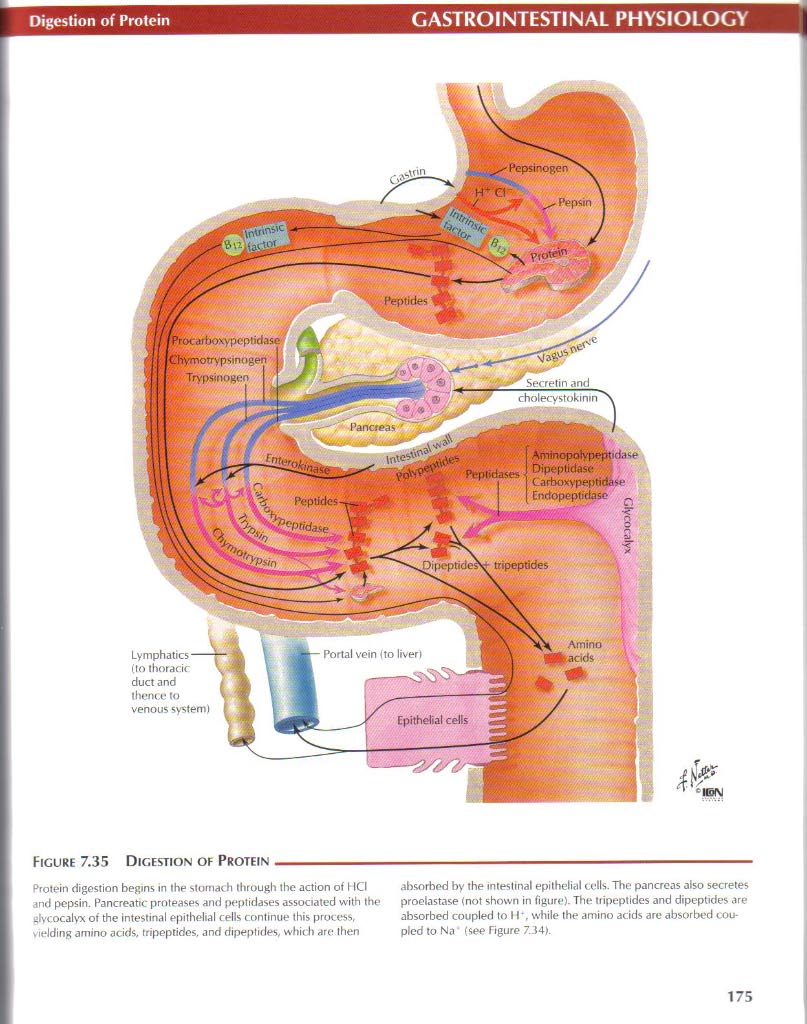
Digestion of Protein
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY
•Pepsinogen
Peptides
Jjpócarboxypcptidase
gpymotrypstmigen
SpTrypsinogen
■-■lir. .• ’ i■ i
cholecystokinin
Partcreas
Peptidases
Peptfdeś-
^PWase
Aminopołyp*ptid.; Dipeptidase ( artx>xypepdt&*e Endopeptićłaso
tripeptides
Lymphatics-
(to lhoradc duet and thencc to venous system)
Portal vein (to liverl
Epitheiial cells
Figurę 7.35 Digestion of Protein_
Protein digestion begins in the stornach through the action of HCI and pepsin. Pancreatic proteases and peplidases associated with the glycocalyx of the intestinal epitheiial cells continue this process, yielding amino adds, tripeptides, and dipeplides, which are then absorbed by the intestinal epitheiial cells. The panereas also secretes proelastase (not shown in figurę). The tripeptides and dipeptides are absorbed coupled to II\ while the amino acids are absorbed cou-pled to Na' (see Figurę 734).
175
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
39605 netter159 Digestion of FatGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Epithelial celi KEY Triglycerides (longa
netter158 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Digestion of Carbohydrales Maftose Pancreatic amyiase
jff 116 DIGEST OF GENERAL RULES FOR JUDO CONTEST It is commonly reąuired in Judo contest that the pl
netter161 Overview of Hormone ActionENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Steroid Hnrmones Thyroid Hormones Vita
netter162 Regulatinn of Hormone Secretion ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Negative Fccdback Hypolhalamus V Targ
netter180 Actions of InsulinENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 8.20 Actions of Insulin- Insulin is a fueł-s
netter190 Whcn words alone won t do, think NetterNetter s Atlas of Humań PhysiologyJohn T. Hansen, P
netter55 Slructure of the HeartCARDIOYASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Mitral valve Poslerior cusp- Ascending aort
netter70 Monitoring of Blond PressureCARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Low-Pressure Baroreceptors ANP releas
netter82 Nłedianics of Respiration: Elastic Properties IRESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY During a slow expirat
więcej podobnych podstron