DSC07968
125
Texlural ditersity of fluual iepow*
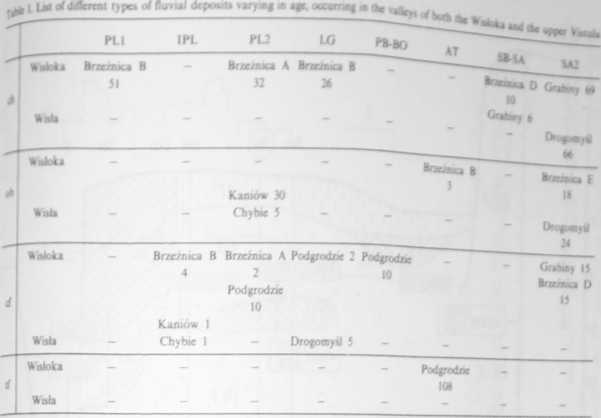
Abbrcviations - type of deposit: di - chanod deposit, ob - overbaok depoui d - duaad fili óepout, tf - dkmal ba iepou?. age designations PL1 - Oldcr PlenigiaaaL IPL - Intcrplcniglacul, PL2 - Youngrr Plemgbaal. LG - I PS-BO - Preborcal-Borcal. AT - Atlantic. SB-SA - Subborcal-Subatlantic. SA2 - Youngcr Subatłaadc Ic bet millenium) Sam ber mdicitet the total number of iamplcs.
yalley which extends in the subsiding mountain foreland represents an other type of sedimentation during which the vertical accretion of the vaUey floor was dominant (Niedziałkowska et al. 1985).
SELECTED EXAMPLES OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF FLUYIAL DEPOSITS
On the basis of the detailed analysis of sedimentary structures, of the macroscopic grain size determination in the deposits, of the spatial distribution of strata and of their location in the vertical profile different types of fluvial deposits have been determined. Additions are the results of grain size analysis and the location of samples on the CM Passega diagram.
Brzeźnica A — There occur typical sandy braided river deposits dating from the Younger Pleniglacial (Fig. 4). These are medium and fine sands including laminae of dusty sands, and even of clayey dusts (Fig. 5). Mz ranges from 1.3 to 3.2 0. Sorting improves upward from poor (<t, = 1.6) to well (a, = 0.4). The laminated dusty sands are characterized by Mz = 4.6-7.0 0. They are very poorly sorted (o, = 2.5). Stratification of the deposits is less well developed, only some strata show a horizontal lamination. Strata decrease upward in thickness (Fig. 5). Pro pert ies of the deposits indicate a channel environment with decreasing dynamics. Both individual strata and mean grain diameters become reduced upward (Fig. 5).
Brzeźnica B — Worthy of notę are channel deposits (a bar) which have been laid down by the meandering river in lateglacial times. These deposits are extensively exposed in a cross-section, some 200 m long (Fig. 4). The deposits show predominantly a tabular cross-bedding, locally alternating with a horizo-
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
125 Hydrological conseąuences of human action.. infiltration into soil and restrict overland flow. R
DSC07904 263 icree ods. The thickness of deposits is often between 5-1 Om (some 17
DSC07929 (2) Geographical Studies Evotution of tbe Yistula Rtver Yalley PL ISSN 0209-1583 TADEU
DSC07952 Geogruphical Studies Evolution of the Vistula Rłver Valley PL ISSN 0373-6547 DOROTA
DSC07962 Geographical Siudies Evołuńon of ihe Ytstuła Rier Yalley PL ISSN 0373-6547 EWA N1EDZIA
DSC07963 120 E. Niedziałkowska 2) characteristics of both grain size and abrasion
DSC07974 ,blc 3- Textural dwersiiy of fluvial deposits Minimum and ma.iminn values of both grain siz
DSC07986 (2) rctchiiif condiuions conccming cithcr thc prcvalenee or absence oi somę. of deposit. Ho
288 decayed rock in sini. At a lieight of 4 meters, the aUuvia give evidence of a deposition through
288 decayed rock in sini. At a lieight of 4 meters, the aUuvia give evidence of a deposition through
w25G The Siena army at the Battle of Val di Chiana on a wall-painting by Lippo Vanni, c. 1
NPL Report MATC(A) 164 curves coincide for displacements less than ~125 pm. For higher levels of dis
Personal financial planning in Poland against llic background of international cxperiencc 125 Table
by treating arbitrary forces as a series of rotating forces 125]. Kinetostatic strains have been con
125 PHOTOELAST X CITY A Rapie method for the determination of principal stresses across secticns of
729 Biuletyn Informacyjny PTMTS 125. B. Raniecki, Ch. Lexcellent, RL-models of
DIŃNAGA ON TR1KALA PARIK$A : AN EXPLORATION INTO SOME AVENUES... 125 philosophy, for^this sort of in
więcej podobnych podstron