2949775324
Comparison of Liąuid Propellant Rocket Engine Feed Systems - 1 - 10
mee
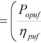
1
SLV
(2.4.3)
Replacing the powers, with the help of preceding eąuations, finally yields:
Pcmp
(2.4.4)
It is necessary to denote that a similar expression can be obtained by the same procedurę, considering a system where each pump is driven by individual motors.
2.5. Inverter mass
As above, beginning with defming the electric motor efficiency, with the same approach applied for the pumps case, will allow relating the inverter output power with the power consumed by the pumps:
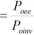
(2.5.1)
In the same way, the inverter power density relates its output power with its mass:
Sinv =
(2.5.2)
In this way, from the two above eąuations, from 2.4.1 and with the same arguments that in the preceding paragraph the inverter mass is estimated in the following way:
mit|v
Pcmr f ai
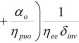
(2.5.3)
2.6. Batteries mass
The batteries are limited in both their energy and power capacity; therefore, the mass must be estimated accordingly with the most restricting factor. Then, two batteries merit factors are defined:
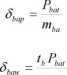
mHa
where, Sbap: Batteries power density (W/kg). Show: Batteries energy density’ (J/kg).
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Comparison of Liąuid Propellant Rocket Engine Feed Systems - 1 - 3 I. INTRODUCTION Since several dec
Comparison of Liąuid Propellant Rocket Engine Feed Systems -1-9 At this point, is convenient to refe
Comparison of Liąuid Propellant Rocket Engine Feed Systems - 1 - 11 According to the previously expo
Comparison of Liąuid Propellant Rocket Engine Feed Systems - 1 - 12 Finally, combining the above exp
Comparison of Liąuid Propellant Rocket Engine Feed Systems - 1 - 15 The turbinę inlet gases are to a
Comparison of Liąuid Propellant Rocket Engine Feed Systems - 1 - 16 3.7. Materials It is necessary t
Comparison of Liąuid Propellant Rocket Engine Feed Systems - 1 - 1 REPORT N21COMPARISON OF LIOUID PR
Comparison of Liąuid Propellant Rocket Engine Feed Systems -1-2 CONTENTS I.
Comparison of Liąuid Propellant Rocket Engine Feed Systems - 1 - 4 current from the battery to altem
Comparison of Liąuid Propellcmt Rocket Engine Feed Systems - 1 - 5 where, my. Pressurizing gas mass
Comparison of Liąuid Propellant Rocket Engine Feed Systems - 1 - 6 0/F mf pfvf - -mp = mppa \+OIF) 1
Comparison of Liąnid Propellant Rocket Engine Feed Systems - 1 - 8 2.2.2. Propellant tank mass In a
Comparison ofLiąuid Propellant Rocket Engine Feed Systems -1-7 (N II £ (2.2.2) where, Ap: Sphere
Comparison ofLiąuid Pr opel fant Rocket Engine Feed Systems - 1 - 13 . gg-RTin (2.9.4) where, Rgg: T
Comparison ofLiguid Pr opel font Rocket Engine Feed Systems - 1 - 14 For each calculation routine, i
Comparison ofLiąuid PropeUant Rocket Engine Feed Systems - 1 - 17 Figurę 2: Synchronous motor specif
Comparison ofLiąuid Pr opel lani Rocket Engine Feed Systems - 1 - 18 Table 6: Proposed batteries t
Research Report.ELECTRIC FEED SYSTEMS FOR LIQUID PROPELLANT ROCKET ENGINES.Pablo Rachov, Hernan
RESEARCH REPORTSELECTRIC FEED SYSTEMS FOR LIOUID PROPELLANT ROCKET ENGINESPablo RACHOV LABORATO
więcej podobnych podstron