
Implementing a Performance
Management System
Change Management and
Performance Management
Performance Continuum
2
•
Misalignment between effort and expected results
•
Poor quality of management reporting - tons of data, negligible information
•
Slow response, information flow
•
Management dissatisfaction
•
Staff dissatisfaction
•
Further customer disenchantment
Emerging Issues
Inflexible, out of date legacy systems
High system / process operating costs
Demand driven need for faster response, rapid product
evolution
Drive for growth
Need for multi site knowledge integration, due to growth,
acquisition, globalisation
Today
Performance
World
Class
Baseline
•
Refined control systems
•
Process orientated
rewards & recognition
•
Further integration to
customers / suppliers,
extended enterprise
•
Focused process
management/leadership
style
•
Process ownership
•
Establishment of new
performance measures for
operations and systems
•
User skill development
•
Alignment of strategic
demands, operational needs
and system functionality
•
Better response times
•
Faster decision making
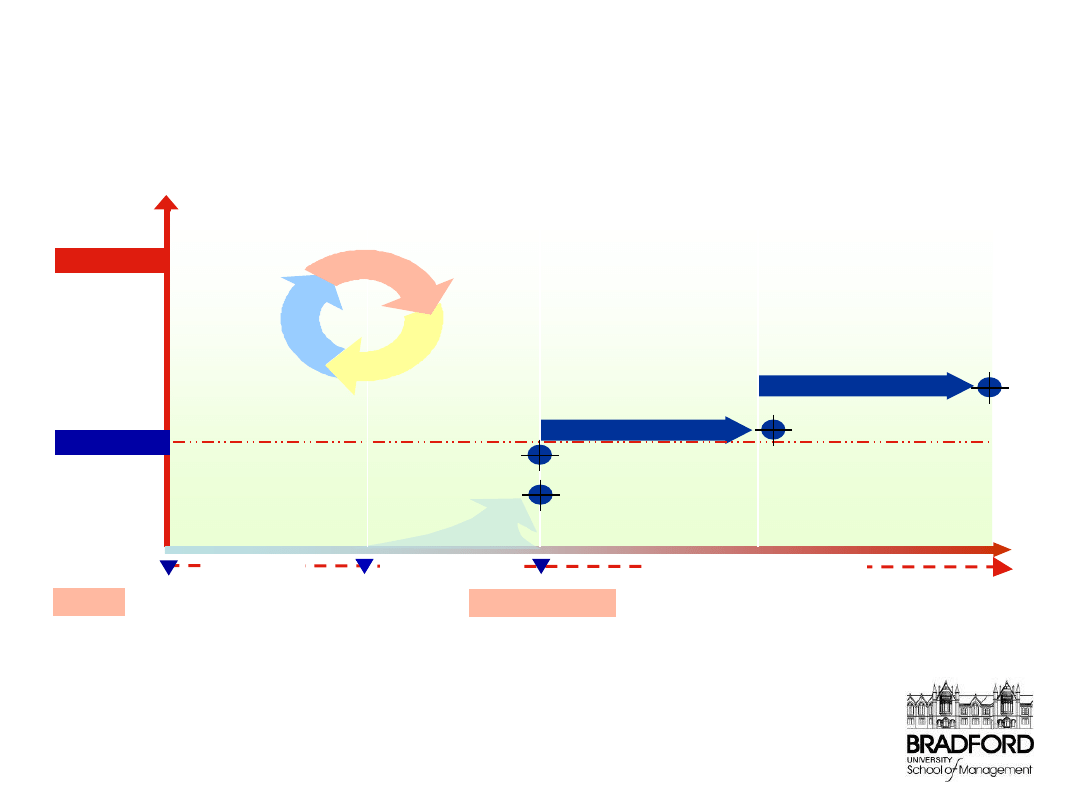
Stage 2 Performance enhancement
Stage 1 Optimisation
Decision
Implementation
Continuous Development
Expected
Delivered
People
Go Live
Process
System
Capability
3
Knowledge
Behaviour
Feelings
Capability
4
Change Management and
Performance Management
Change Management is the planning, initiating and
managing of changes to processes, behaviours and
attitudes in an organisation.
When implementing a Performance Management system across an
organisation, it is often forgotten that a complex web of conditions and
emotions must be accomodated:
Ability to
Change
Personal
Cost
Need for
Change
Willingness
to Change
Financial
Cost
+
+
+
>
5
When does Change Management
Come into play?
Triangle
of
balance
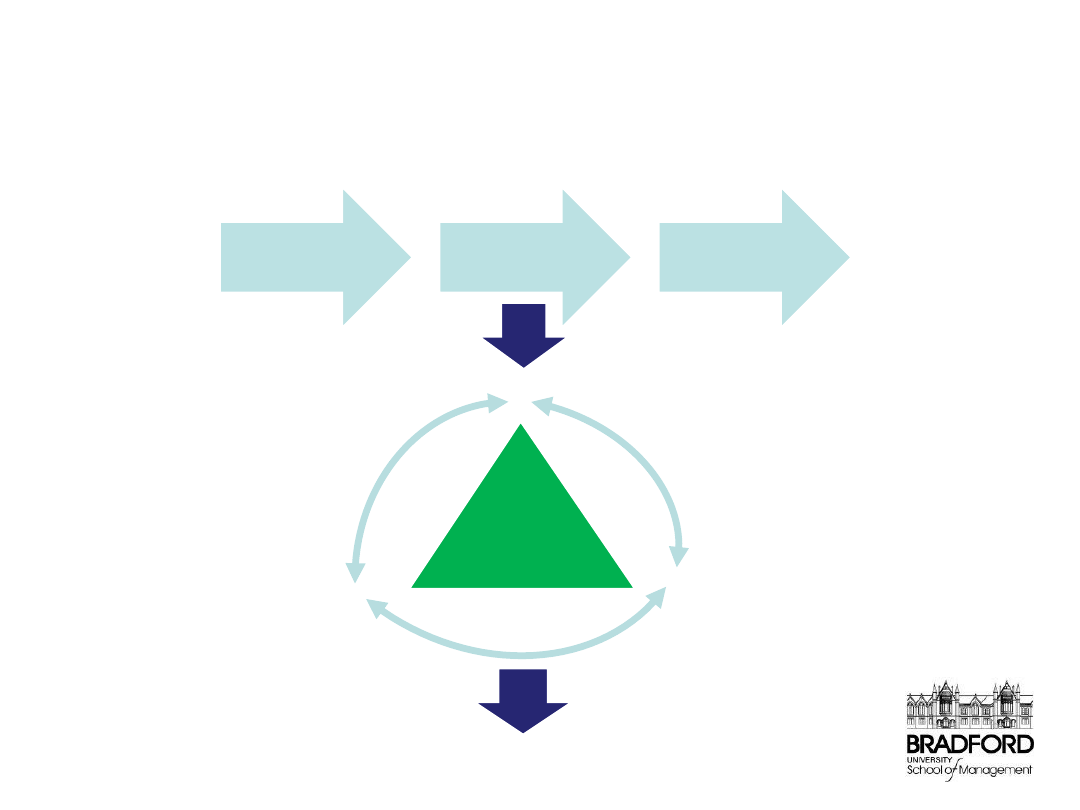
The business need
Definition
Timescale
Cost
Performance
management
requires……
…capability
which permits…
….benefit to be
delivered
6
Organisational Change Axes
The implementation will tend towards one or other of the axes unless executive and
management have clear and shared objectives, and are fully committed to rigorous
performance management.
Efficiency
Culture change
“the long march”
…..behaviours/attitudes
££s
only
What information do
we need to manage
the business?
What do we need
to do to our
systems to deliver
this information?
How do we adjust
our processes to
avoid GIGO?
Let’s deliver the
changes...
... but pilot
them first
A classic three-step approach
Data massaged
into a common
format
New
“Data
Warehouse”
Operational systems with
enhancements
Operational &
Financial
data
Direct feeds
What needs to happen
New EIS

What needs to happen
– Get consensus. It takes time, but the process of
getting consensus is actually valuable
– Reality test the measures as early as possible: what
is the cost/benefit?
– Think ahead and build for flexibility
– Communicate, communicate… and communicate
– Get all necessary contributors on board as early as
possible
– At times, someone has to just drive things through –
get a good sponsor!
10
The Characteristics of Change
Kübler-Ross Change Curve
Shock
Valley of
despair
Denial
Awareness
Acceptance
Integration
Experimentation
Search
The Emotional Cycle of Change
Pe
rc
eiv
ed
Compete
nce
Time
11
Bringing it all together
Stage
1
Stage
2
Stage
3
Stage
4
Recognition of need to change
Competitive Arena
Change Definition:
Mission and Goals
Choice of strategy
and tactics
Implementation
and evaluation
Operational Efficiency
Market Effectiveness
Top Managers
Senior Managers
Managers and
supervisors
Supervisors and
workers
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
lecture 11
lecture 11 attribute charts id Nieznany
Lecture 11
lecture 11 http ftp
Lecture 11 12 C
lecture 11
11 26 listening CHANGES
Lecture 11, Epping, Dług publiczny, rozszerzony
11 07 U2 change synonyms
Summary of lectures 11 12
Lecture 11 Operating systems
11 Dribbling and Changes of Direction
BIO110 lecture 33 (11 10 10)
Econometrics, Lecture 4, 2014 03 11
LECTURE 3 ATTACHMENT 1 PMs of Great Britain
Changelog 17 11 07
Changeling The Lost Errata July 11 08
więcej podobnych podstron