Reactions of Alcohols
hydrogen bond (wiązanie wodorowe)
toxic (toksyczny)
elimination of water (eliminacja wody)
sodium (sód)
alcoholate (alkoholan)
Alcohols undergo combustion with O2 to produce CO2 and H2O.
2CH3OH + 3O2 2CO2 + 4H2O + Heat
Dehydration removes H- and -OH from adjacent carbon atoms by heating with an acid catalyst.
H OH
| | H+, heat
H—C—C—H H—C=C—H + H2O
| | | |
H H H H
alcohol alkene
Zaitsev's rule - dehydration of alcohol normally forms the alkene with the more highly substituted (or more highly branched) double bond. B/c of stability
EASE OF DEHYDRATION
1o alcohols 2o alcohols 3o alcohols
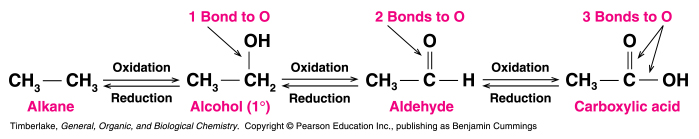
Oxidation of Alcohols
1°alcohols are oxidized to aldehydes and 2° alcohols are oxidized to ketones
Formation of Alkoxide Ions
React methanol and ethanol with sodium metal (redox reaction).
Esterification
The esterification process produces esters through a condensation reaction. Condensation reactions have water as one of the products. The reactants for esters are an alcohol and an acid (either an organic or an inorganic acid). A catalyst, such as concentrated acid

The esters are named as salts of the acids prefaced with name of the alcohol. Examples are shown in the chart.
Alcohol |
Acid |
Ester |
Odor |
methyl |
acetic |
methyl acetate |
sweet |
ethyl |
acetic |
ethyl acetate |
fruity |
isoamyl |
acetic |
isoamyl acetate |
banana |
isoamyl |
butyric |
isoamyl butyrate |
pear |
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
materialy z alkoholi Nomenclature and Structure of Alcohols
Eurocode 6 Part 2 1996 2006 Design of Masonry Structures Design Considerations, Selection of Mat
Material related aspects of the machinability of Austempered Ductile Iron
Eurocode 6 Part 2 1996 2006 Design of Masonry Structures Design Considerations, Selection of Mat
EMOCJE, Interesujące, PSYCHOLOGIA, PSYCHOLOGIA (materiały), alkoholizm - materiały
Poczucie winy jak się go pozbyć, Interesujące, PSYCHOLOGIA, PSYCHOLOGIA (materiały), alkoholizm - ma
CO TO JEST PSYCHOTERAPIA UZALEŻNIENIA, Interesujące, PSYCHOLOGIA, PSYCHOLOGIA (materiały), alkoholiz
Poczucie krzywdy i przebaczanie, Interesujące, PSYCHOLOGIA, PSYCHOLOGIA (materiały), alkoholizm - ma
ZALECENIA DLA ZDROWIEJĄCYCH ALKOHOLIKÓW, Interesujące, PSYCHOLOGIA, PSYCHOLOGIA (materiały), alkohol
GŁÓD ALKOHOLOWY, Interesujące, PSYCHOLOGIA, PSYCHOLOGIA (materiały), alkoholizm - materiały
ALKOHOL W RODZINIE, Interesujące, PSYCHOLOGIA, PSYCHOLOGIA (materiały), alkoholizm - materiały
Wstyd i poczucie winy, Interesujące, PSYCHOLOGIA, PSYCHOLOGIA (materiały), alkoholizm - materiały
EMOCJE, Interesujące, PSYCHOLOGIA, PSYCHOLOGIA (materiały), alkoholizm - materiały
Decomposition of Ethyl Alcohol Vapour on Aluminas
A protocol for polymerase chain reaction detection of Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faec
13 161 172 Investigation of Soldiering Reaction in Magnesium High Pressure Die Casting Dies
5 kinetic of bioleaching reaction
Treatments of Alcoholism
więcej podobnych podstron