F00574 014 g002
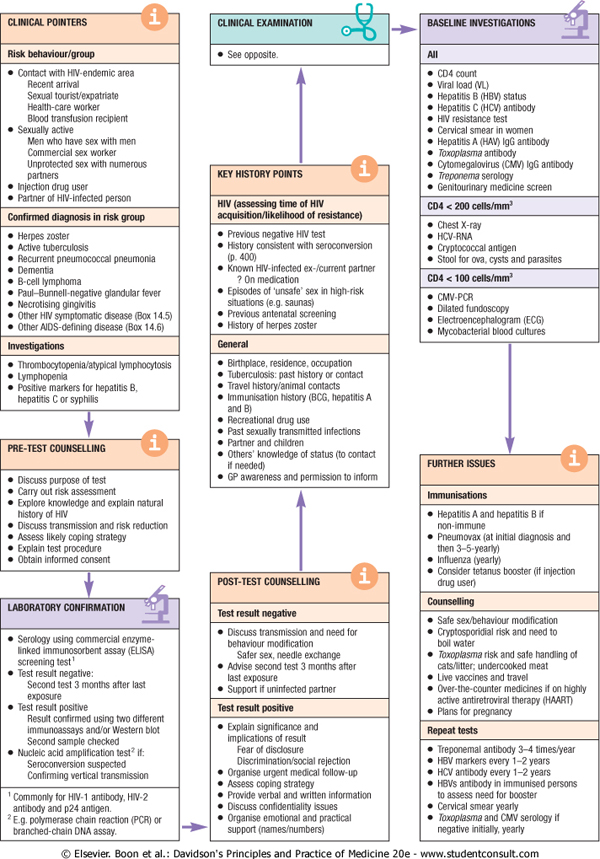
CLINICAL POINTERS
CLINICAL EXAMINATION
BASELINE INYESTIGATIONS

Risk behayiour/group
See opposiie
AJI
• Contact wrth HfYendemic area
Recent arrivai $exuai tourisitopatriate Heanh-care worker BJood traretuston reclpłem
• Sexualiy aclue
Men who have sex with men Commercial sex woiker Unproteded sex with numerous partners
• mjection drug user
• Partner d Hiv-lnfected person
KEY HISTORY POINTS
Confirmed diagnosis in risk group
HIV (assessing time ol HlV acguisition/likdihood of resi stance)
• CD4C0unt
• Virai load (VI)
• Hepatite B (HBV) status
• Iłepatios C (HCV) antibody
• nv resistance test
• Cervlcal smear in women
• tfepatihs A (HAV) igG antibody
• Toxopła$ma antibody
• Cytomegakn/lrus (CMY) IgG antibody
• Treponema serology
• Genitounnary mediwie screen
C04 < 200 ceUs/mm’
• Herpes zoster
• Actlve tubcraitoss
• Recurrent pneumococcal pneumofra
• Demenba
• B-cell lymphoma
• Paul-Bunnell negative glandufer tever
• Necrotlslng gingivitls
• Other hiv symptomatic cfcsease (Bo* 14.5)
• Other AJDS-detining dtsease (Box 14.6)
lnvestigations
• Tt¥omt)ocytopenia/atypjcaityniphocyiosis
• Lymphopenia
• Pasitiye markers lor hepaiihs B. hepatits C or syphihs
• Previous negative wv test
• Hcstory consistenl with serocorwcrsion (p 400)
• Known HfV-intected ex-/current partner
? On medcation
• Eptsodes ot 'unsafe' sex m high risk srtuattons (e g saunas)
• Previous antenatai screening
• Mtstoiy d herpes zoster
General
• Chesi X-ray
• HCV-RNA
• Cryptococcal antigen
• Stoolforova,cystsandparasites
C04 < lOOcelłs/mm’
• CMVPCR
• Dilated fundoscopy
• Electroencephaiogram (ECO
• Mycobactenal Wood cultures
PRE-TEST COUNSELLING
Oiscuss purpose d test Carry out rtsk assessment Exptixe knowtedge and exptain naturai rustocy ot hiv
Oiscuss transmission and risk reduction Assess likety coptng strategy Explam test proceduro OMaln inlormed consent
i
LABORATORY CONFIRMATION

• ftrthptace, residence. occupatlon
• Tuberculosis: past history or contact
• Travel history/animal contacis
• Immunisation history (BCG. hepatflls A and B)
• Recrealional drug use
• Past sexuaiiy transmltied infecbons
• Partner and cfokken
• Others’ kncwledge ot status (to contact if needcd)
• GP awareness and permission to inform
POST-TEST COUNSELLING
FURTHER ISSUES
Immunisations
Hepatibs A and hepatltis B if nonimmune
Pneumovax (at Iniuai dagnose and then 3-5-yearty)
Influenza (yearly)
Consrder tetanus booster (if injcction drug user)
Counsdlmg
Serology using commeroal enzyme-inked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) screening test'
Test resutt negatlve:
Second test 3 months atter last exposure
Test resutt positrve Resiit contirmed using two diflerent immunoassays aiktfor Western biot Second samplo checked Nucleic acid amplilication test7 łf: Serocoiwersion suspected Confirming vertical transmission
Test resutt negatńre
• Oiscuss transmission and need for behaviour modilication
Sater sex, needie exchange
• Advtse second test 3 months atter last exposure
• Support ii uninlected partner Test resutt positive
Safe sex/behaviour modification Cryptospońdiai risk and need to boil water
Toxoptosma risk and sale handling ol catsłtter: undercooked meat Lwe vaccmes and travei Orerthe-counter medicines (1 on highty actwe anhretrowrai therapy (HAART) Plans for pregnancy
' Commonty lor HIV-1 antibody. i*V-2 antibody and p24 anbgsn.
1 Eg. pdymerase cham reaction (PCR) or branched-chain ONA assay.
• Expłain signilicance and Impiicatlons d resutt
Fcar d disdosure Dłscrlmlnation^sociai re|ection
• Organise urgent medcat follow-up
• Assess copmg strategy
• ProYide verbai and wrltten information
• Oiscuss conhdenbaiity ssues
• Organise emotionai and practical support (names/numbers)
Repeat tcsts
Treponemai antibody 3-4 times/year IBV markers every f-2 years HCV antibody every 1-2 years HBVs antibody m Immunised persons to assess need for booster Cemlcal smear yearty loxopiasma and CMV serology ii negatwe ritialty, yearty
<$> Elsevier. Boon et a!.: Dayidson^s Principles and Practice of Medicine 20e - www.studentconsult.com
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
F00574 019 g002 ©-© KEY FEATURES ON EXAMINATION OF COMMON RESPIRATORY CONDITIONSChronić obstructive
F00574 018 g002 o EXAMINATION OF THE ARTERIAL PULSE • The character of the pulse i
F00574 022 g002 ABDOMINAL EXAMINATION: POSSIBLE FINDIN6S Left upper guadrant mass ?Spleen Edge
Finał (clinical) examination results 2009 - 2012 Australia New
F00574 007 g002 © GET UP AND GO TEST Ask the patient to stand up from a sitting position, walk 10 m,
F00574 008 g002 lntravenous fluids Monitor displaying biood pressure/ atnai pressure/heart
F00574 014 f001 Stagc Steps in rcplication Drug targcts 1 Attachment to CD4 receptor 2 Binding to
F00574 014 g001 Oropharynx Teeth Periodontitis Mucous membranes Herpes simplex Aphthous ui
F00574 023 g002 CAUSES OF A8N0RMAL LtVER SI2E o FLAPPING TREMOR Jerky forward morements every 2-3 se
F00574 024 g002 o ANAEMIA The box shows the symptoms and signs that will help to indicate the d
Examinati.pn NpUccEmgrammfi nŁDegatcd (limisj Group Pistribution; Group- A: Physics. Chemistry. Boła
F00574 003 f007 □ oo 0 d. 50 y Małe. female. unknown sex Clinically affected (specify condition in k
F00574 005 f015 Total - 0 Total = 1 Total £ 2 Low risk Medium risk High risk • Routine clinica
F00574 018 f017 Stable angina Unstable angina Pathophysiology Clinical features Risk assessment •
F00574 007 f002 Changes with ageing Clinical conseguences CNS • Neuronal loss •
65679 Tabela 1 labie L Baseline Clinical and Angiographic Core Laboratory Characteristics.* Charac
więcej podobnych podstron