F00574 023 g002

CAUSES OF A8N0RMAL LtVER SI2E
o FLAPPING TREMOR

Jerky forward morements every 2-3 seconds when arms are outstretched and hands are dorsiftexed.
0 PALPATION OF THE ABDOMEN
Livcr
• Start in the right iliac fossa.
• Progress up the abdomen 2 cm with each breath (through open mouth)
• Confirm the lower border of the liver by percussion (see 6).

• Detect if smooth or irregular. tender or non-tender; ascertain shape.
• Identify the upper border by percussion (see 6).
Large lim (hepatomegaly)
• Liver metastases
• Cirrhosis
AJcohoi
Kaemochromatoss
• Hepatic venous outnow obsiruction
Smali lim
• Cirrhosis
Auiołnmutw lim dtsease Alpha ,-antitrypsin defidcncy Cryptogenic
|
CAUSES Of ASCITES | |
|
High protein (exudative) | |
|
• Carcinoma | |
|
• Tuberciiosis | |
|
Low protein (transudative) | |
|
• Congestrvc heart faiiure | |
|
• Renal faiiure (induding | |
|
nephrotic syndrome) | |
|
• Cirrhosis | |
0 PERCUSSION OF THE ABDOMEN
Liver
• Ahvays start percussion from resonant to duli; i.e. percuss lower border from benoath and upper bordor from above.
• Percuss the abdomen gently. the chest morę firmly.
• Once the upper border of tho liver is idontified. confirm its position by counting down the ribs from the sternal angle (second mtercostai space).
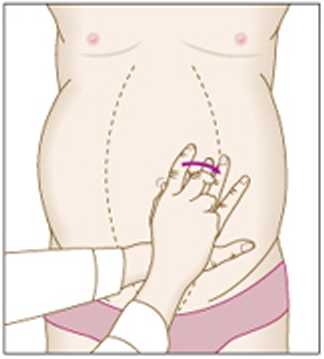
Shifting dullncss
• Start around the umbilicus (resonant).
• Percuss at 1 cm intorvals around to the left flank.
Spleen
• Start again in the right iliac fossa.
• Progress towards the left upper quadrant at 2 cm intervais.
• Place the left hand around the lower laterai ribs as the costal margin is approached.
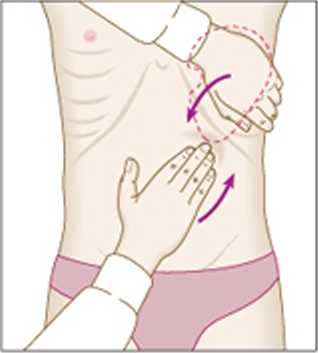
• Notę the charactenstics of the spleen
- Notch
- Superfioal
- CHJI to percussion
- Cannot get between ribs and spleen
- Moves wen with respiration.
• identify where duiiness occurs.
• Roli the patient on to the left-hand side and notę if the level of dudness moves towards the umbilicus.

© Elsevier. Boon et al.: Davidson's Principles and Practice of Medicine 20e - www.studentconsult.com
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
F00574 018 g002 o EXAMINATION OF THE ARTERIAL PULSE • The character of the pulse i
F00574 019 g002 ©-© KEY FEATURES ON EXAMINATION OF COMMON RESPIRATORY CONDITIONSChronić obstructive
F00574 024 f006 Neutrophil Causes of neutrophilia Causes of
IMGG44 (3) Leading Causes of DeathPercenłage by Subgroup: Ca nada. 1994CanftMscuto 38% V»oience 0% T
F00574 004 f006 Failure of thymic development: DiGeorge syndrome Failure of expressiorn of HLA
F00574 004 f007 Failure of production of IgG antibodies: Common variable immune deficiency Spec
F00574 004 f010 Feeling of impending doom, loss of consciousness Angioedema of lips and mucous membr
F00574 007 g002 © GET UP AND GO TEST Ask the patient to stand up from a sitting position, walk 10 m,
F00574 008 g002 lntravenous fluids Monitor displaying biood pressure/ atnai pressure/heart
F00574 009 f002 Routes of cxposurc to toxinsDirect eye contact Eye Eye irrigationMethods of preventi
F00574 014 g002 CLINICAL POINTERS CLINICAL EXAMINATION BASELINE INYESTIGATIONS Risk behayiour/group
F00574 015 g001 Skin of penis (Retract prepuce if present) Genital warts Ulcers Be aware oł nor
F00574 019 f026 Enlargement of mucus-secreting glands and inerease in number of goblet cells, a
F00574 019 f030 FEV, (% of value at age 25) Never smoked or not susceptible to smoke Stopped ■smokin
F00574 020 g003 o EXAMINATION OF THE THYROID GLAND • Inspect from front to side •
F00574 022 g002 ABDOMINAL EXAMINATION: POSSIBLE FINDIN6S Left upper guadrant mass ?Spleen Edge
F00574 023 f004 Central vein Portal vein Zonę 3 (pericentral) Zonę 2 Zonę
F00574 023 f019 (D Sinusoidal @ Intrahepatic pre-sinusoidal (5) Extrahepatic pre-sinusołdal © Elsevi
F00574 023 f026 HBV-tolerant HBV clearance Latent phase HBV mutant Cirrhosis © Elsevier. Boon et a
więcej podobnych podstron