Funkcje cyklometryczne zad1
28
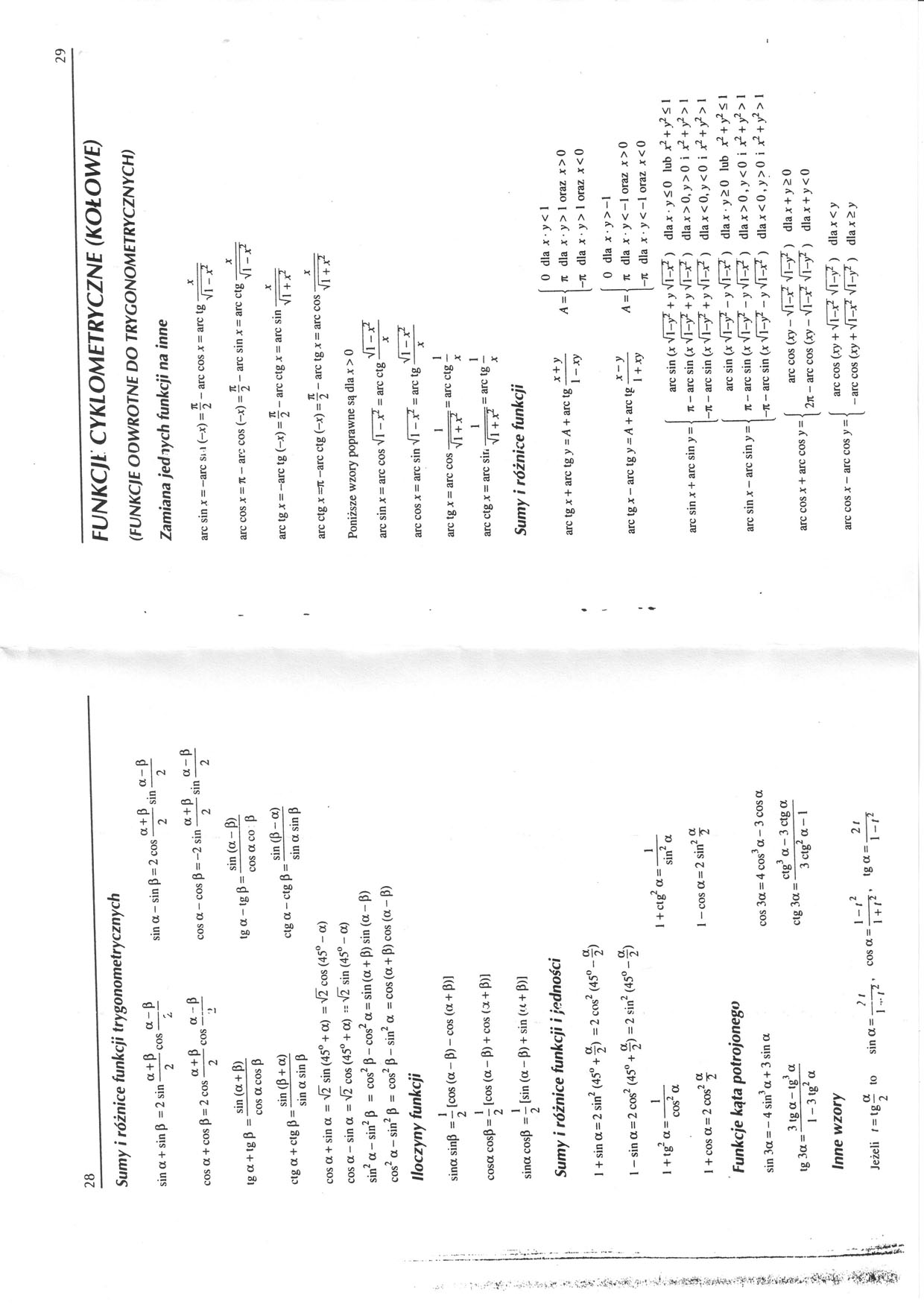
Sumy i różnice funkcji trygonometrycznych
28
„ a+P a-p
sin a + sin P =2 sin-cos--
’ ”■> <*
Ł /.
a+P a-p sin a - sin p = 2 cos-sin-
cos a + cos 3 = 2 cos
a + p a-p
tg a + ig p =
2
sin (a + 3) cos a cos p
cos a - cos p = -2 sin
a+p . a-P
tg a - tg p =
sin (a - P) cos a co 3
„ sin (3 + a)
ctg a + ctg 3 = -;-—
sin a sin 3
„ sin (3 - a)
ctga-ctgp = --—
sin a sin p
cos a + sin a = V2 sin (45° + a) = V2 cos (45° - a) cos a - sin a = Ś2 cos (45° + a) ■-'Ii sin (45° - a) sin2 a - sin2 p = cos2 P - cos2 a = sin (a + P) sin (a - P) cos2 a - sin2 p = cos2 p - sin2 a = cos (a + P) cos (a - P) Iloczyny funkcji
sina sinP = - [cos (a - 3) - cos (a + 3)]
cosa cosP = - [cos (a - 3) + cos (a + 3)]
2
sina cosP = — [sin (a - 3) + sin (a + 3)]
Sumy i różnice funkcji i jedności
I + sin a = 2 sin2 (45° + f) = 2 cos2 (45° -1) I - sin a = 2 cos2 (45° + f) = 2 sin2 (45° - f)
1 +tg-a = —— cos a
, 1
I + ctg a = —y
1 + cos a = 2 cos'
2 a
. , .ja
I - cos a = 2 sin -j
Funkcje kąta potrojonego
sin 3a = - 4 sin3a + 3 sin a
3 tg a - tg3 a
tg 3 a =-5—
I - 3 tg2 a
Inne wzory
cos 3a = 4 cos3 a - 3 cos a ctg3 a - 3 ctg a
ctg 3a = -
3 ctg2 a - 1
a 2/ l-r 21
Jeżeli f = tg— to sina =--, cosa =-y, tga = --*
6 2 I-/2 1 +f2 l-/2
FUNKCJE CYKLOMETRYCZNE (KOŁOWE)
(FUNKCJE ODWROTNE DO TRYGONOMETRYCZNYCH) Zamiana jednych funkcji na inne
arc sin * — -arc Si i (-*) = - arc cos x = arc tg . —
2 Vl -*2
arc cos x = Tl - arc cos (-*) = j - arc sin x = arc ctg ,, 2 Vl - jr
7t X
arc tg x = -arc tg (~x) = -x - arc ctg x = arc sin .
2 Vl + X1
arc ctg x =71 -arc ctg (-*) = -x - arc tg x = arc cos . .
2 Vl + xr
Poniższe wzory poprawne są dla x > 0
fi—U Vl — jr2
arc sin jt = arc cos v 1 - xr - arc ctg —-—
arc cos x = arc sin Vl -X1 = arc tg
arc tg jr = arc cos
arc ctg x = arc sir.
arc tg x + arc tg y = A + arc tg
0 dla jc • y < I
A = i 7i dla x ■ y > 1 oraz jc > 0 |—7i dla x ■ y > I oraz Jt < 0
arc tg x - arc tg y = A + arc tg
arc sin x + arc sm y =
arc sin x - arc sin y =
arc cos x + arc cos y =
0 dla x ■ y >-l
A = Tl dla x ■ y<-l oraz x >0 —71 dla Jt • y < -1 oraz x < 0
arc sin (jr Vl-y* +y V1 —jr^ ) dlax y<0 lubj^ + y^SI Ti - arc sin (x Vl-y2 + y VI-.*2 ) dla * > 0, y > 0 i ot2 + y2 > 1 -Tl - arc sin (* V l-y2 + y VT-7 ) dla * < 0, y < 0 i x* + y2 > 1 arc sin (* VI —y2 - y Vl-*2 ) dla * • y 5 0 lub jt2 + y2 <, 1 Jt - arc sin (* Vl-y2 - y VI-*2 ) dla*>0,y<0i*2+y2>l —7t - arc sin (* VI —y2 - y VI-*2 ) dla*<0,y>0i*2 + y2>I
arc cos (*y - VI-*3 VI —y2 ) dla * + y 2 0 2n-arccos(*y-VI-*3 Vl-y2 ) dla* + y<0
*-y
I +xy
arc cos (*y + Vl-*2 VI—v2 ) dla * < y arc cos * - arc cos y = i .—_ .—1_
-arccos(*y + Vl-*2 Vl-y2 ) dla*>y
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
MATEMATYKA ■ą FUNKCJE TRYGONOMETRYCZNE ■1 SUMY I RÓŻNICY KATÓWii wKmKKMiii
19 Funkcje trygonometryczne sumy i różnicy kątów: cos(0j + 02) = C12 = C1C2 - S1S2 sin(0! + 02) = S1
img220 Funkcje trygonometryczne sumy i różnicy kątów Dla każdego *eR, yeR prawdziwe jest: sin (* +
36008 Rozdział II Funkcje trygonometryczne Rozdział II FUNKCJE TRYGONOMETRYCZNE 1. &nb
Funkcje cyklometryczne wykresy 30WYKRESY FUNKCJI TRYGONOMETRYCZNYCH I CYKLOMETRYCZNYCH Funkcja y =
Funkcje cyklometryczne wykresy 30WYKRESY FUNKCJI TRYGONOMETRYCZNYCH I CYKLOMETRYCZNYCH Funkcja y =
10 WYKRESY FUNKCJI TRYGONOMETRYCZNYCH I CYKLOMETRYCZNYCHTABLICA FUNKC/I
skanuj0029 (15) • Niektóre wartości funkcji trygonometrycznych ar o(o°) f(*) §m f(9T) sin
funkcje trygonometryczne Funkcje trygonometryczne w trójkącie prostokątnym przyprostokątna naprzeciw
Funkcje trygonometryczne zadania I &■ %BS E r$d
więcej podobnych podstron