P5140083
Shin Splint or Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome Combination Technigue
Combining the Kinesio Tcchnique with traditional treatments may proeide both acute pain reduction and long term posifiYe benefits for shin splints or medial tibial stress syndrome.
Scveral examples will be givcn in which the Kinesio Technique will be combined with traditional treatments; Iow dye, longitudinal arch, or orthotics. The practitioner will need to evaluate each patiem and apply whał is in theiropinion the best course of treatment. If one method is selected and the results are not as effective as desired, try another method.
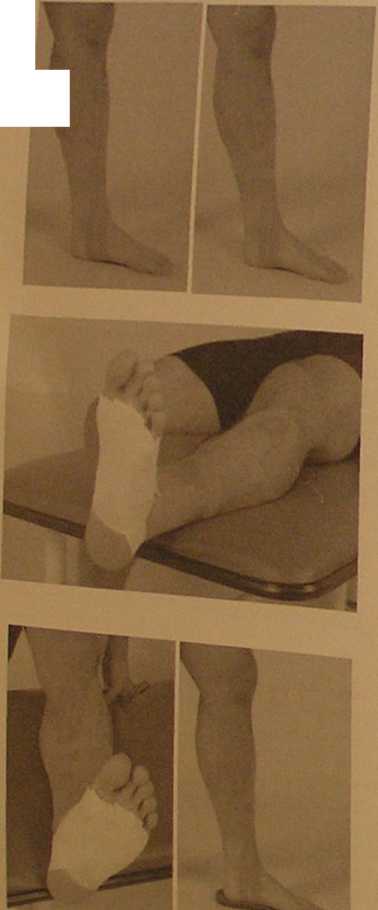
Complcted application of the Kinesio technique for shin splints. Two examples are given.
Photo on Ieft: space correction pulling away from medial border of tibia.
Photo on right: space correction using the baseof the Y to puli tissue to the medial border of the tibia. For complełe revievv see shin splint application technique.
Application of the Kinesio technique for shin splints in combination with a Iow dye technique. For complete review see Iow dye technique, as described in metatarsal arch combination technique.
Photo on Ieft: application of the Kinesio technicjue for shin splints in combination with the longitudinal arch technique. For complete review see longitudinal arch technique, as described in plantar fasciitis combination technique.
Photo on right: application of the Kinesio tech-nique for shin splints in combination with orthotics.
Anterior Compartment Hematoma /Syndrome

An injury to the anterior compartment may result from direct trauma or from a \oss of fascia expan-jion surrounding the four compartments. Each of the four compartments of the lower leg: anterior, lateral. posterior superficial and posterior deep, are surrounded by a fascia which expands during exercise. Each compartment contains muscles, artery, vein and nervous tissue. When an acute trauma occurs a hemmorhage may result decreasing circulation and causing pressure on the nerve. A compartment may also be effected by a decrease in the elasticity of the fascia surrounding the compartment, msulting in an increased pressure causing numbness.
Acute compartment hematomas are treated by reducing the hemorrhage. Chronić exertional compartment syndromes are treated by reducing the increased pressures within the compartment.
For both the acute and excertional compartment syndrome a lymphatic correction will be used to reduce pressure within the compartment. The first lymphatic strip is placed with the base at the medial aspect of the knee just superior to the joint linę.
For complete review see lymphatic correction application technique.

A second lymphatic correction strip may be applied starting with the base located elose to the insertion of the Achille's tendon. The fan tails are overlaid in a crisscross pattem over the first fan strip.
Pj


With an acute hemorrhage resulting in a hematoma, a space correction techniąue may be used. This space correction I strip should provide additional space directly above the hemorrhage allowing for the edema to be removed.
Tear the Kinesio strip paper backing in the middle, apply 15-25% tension to the center of the strip. Apply this central area directly over the hematoma. If appropriate have the patient move into opposite rang of motion, lay down tails with not tension.
For complete review see space correction techniqu<
121
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
P5140082 Shin Splint or Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome The treatment for shin splints is as voried as
P5140054 Elbow Hyperextension Combination Technique Elbow hyperextension combination taping will com
STRESS ANALYSIS Charts for checking the stability of compression members in trusses as of fuselage o
Slide19 (2) Sartorius m Medial femoral condyle Posterior-- Cruciate ligame Medial ^ meniscus Medial
P5140026 Neck Sprain or Whiplash The Kinesio taping technique wili assist with reduction in edema, m
P5140039 Thoradc Outlet Syndrome I Thoradc outlet syndrome is a compression of the
P5140043 Costochondral Separation or Sprain A separation or sprain to the juncfion of the castocarłi
P5140046 Sacroiliac Sprain or Inflammation g ligaments that The sacroiliac joint if formcd by the sa
P5140086 Patella Tendonitis: Superior and Inferior Pole Patella tendonitis at either the superior po
iI crystal, or magnetic—can be employed. Stereo or mono tape recordings can be madę using the monito
1LB 11 TUTORIAL RHYTHM (5) L B April 2<m front HSA STRESS PATTERNS ANALYSE AND DESCR1BE THE STRE
TUTORIAL 3 A STRESS PATTERNS / EXAMPLES Is that the man who sent you the tickets. Ą O HasnT John giv
c Help may also be uscd wilh a fuli infinitive, either alone or afier an object: I helped (them) (to
3cf23240d962e82e9fa6beb1c3dab587 ló authomcd lo bo paid under said Act, or as auŁltorizcd undor 16 t
więcej podobnych podstron