8589356514
FLINT MINING OF CENTRAL EUROPE 21
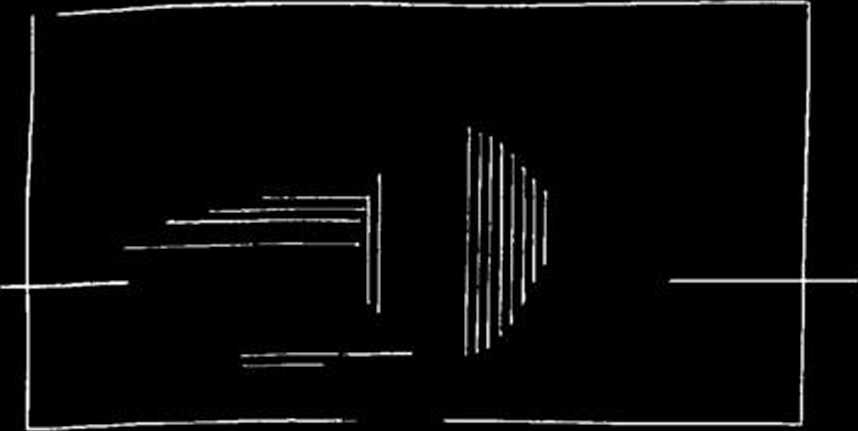
Fig. 20. Gorodok, Rovnc dist. Visncvaya Góra sile
/ — Plan of thc exploitation unit and wastc-hcap; // — Section of exploitation unit and wastc-heap on axis A - B: 1 — pit, 2 - wastc-hcap, 3 — flint workshop,
4 — soi!, 5 — locss, 6 — bcd-rock
Aftcr I.K.Svc5nikov
thc edge of the Corded Ware settlement at thc foot of Viśnevaya Góra. Prcliminary prcpared nodules werc ta-ken there. Stone rctouchers and hammerstones, spherical flint hammerstones, fragments of antler mining tools
Fig. 2!. Gorodok, Rovnc dist. Viśnevaya Góra site. Filnt workshop
from plan in fig. 20, Scalę 20 cm
Photo by I.K.Svc5nikov
and scmiproducts of flint axes and sicklcs come from thc settlement. At a distance of between one half km to 5 km from ViSnevaya Góra morę than 20 other settle-ments of the Corded Ware Culturc have been disco-vered. Some of them provided antler tools for mining works (Sveśnikov 1969, 118).
The facts ascertained by I. K. Svcśnikov i.e.: the prcscnce of local turning up of the soil with waste hcaps accompanying them and workshops of preiiminary Processing as wcli as typical mining tools, which allowed him to characterize thc unit from Visnevaya Góra as a manifestation of the simplest mining. As the abundant comparative materials indicate, the kind of works in the whole prehistorie Europę depended first of all on the deposits’ gcological situation, and was not deter-mined culturally, and secondly we can assume the ex-istcnce of similar extractive units in other regions.
2. SURFACE PITS
Surface working consisted in digging shallow, smali pits with a depth from tens to the maximum approx. 1.5 m and with a bigger diameter not usually exceeding 2 m. Such workings, from the beginning to the end, could have been dug and exploited by one man. From the point of view of working them, obtaining flint from thc pits did not reąuire the participation of any morę pcople. The right kind of planning, the knowledgc of deposit and of mining field were the only things ncccssary.
Typical units of this sort were found on the terri-
Fig. 22. Bębło, Cracow dist. Surface pits (1-3)
a — soil; b — locss containing artefaets and a smali admixture ofeluvial clay which fillcd in thc pit; c — cluvial clay with flinls
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
FLINT MINING OF CENTRAL EUROPE 31 FLINT MINING OF CENTRAL EUROPE 31 Fig. 43. TuSimicc, Chomutov dist
FLINT MINING OF CENTRAL EUROPE 15 Fig. 13. Gorzów Wielkopolski-Chwalęcice. Kłodawka rivcr gap at mor
FLINT MINING OF CENTRAL EUROPE 17 as “chains” (Fig. 16). Very big nodules (approx. 40 cm) are vcry r
FLINT MINING OF CENTRAL EUROPE 27 Fig. 34. Kalvśria Hill. Tata. Section of shaft 2 / - from thc Sout
FLINT MINING OF CENTRAL EUROPE 35 Fig. 51. Rijckholt—St.Geertruid, Maastricht dist. Schematic scctic
FLINT MINING OF CENTRAL EUROPE 41 rounded; the other one is transversely “cut”, for use as a hammer
FLINT MINING OF CENTRAL EUROPE 19 IV. REMARKS ON THE TER MS “MINĘ” AND “MINING” IN THE RESEARCH ON
FLINT MINING OF CENTRAL EUROPE 23 towards this view recently (1971, 120 f.; 1975, 162). As can be se
FLINT MINING OF CENTRAL EUROPE 25 loam laycrs to sandstone. Quartzite was extruded from thc sandston
FLINT MINING OF CENTRAL EUROPE 7 meration in the earth crust could bc rccognizcd as a de-posit. In p
FLINT MINING OF CENTRAL EUROPE 39 1973, 185 187) and obscrvations madę by S. Krukowski at Krzemionki
FLINT MINING OF CENTRAL EUROPE 49 Tablc 2. Radiocarbon dates from other areas of prehistorie flint m
FLINT MINING OF CENTRAL EUROPE 51 sia, in Opava Silesia, and in north-wcst Moravia. Jasper exploitat
53 FLINT MINING OF CENTRAL EUROPE Damon P.E., Łono A. 1962 Arizona Radiocarbon Dat es III, “Radiocar
FLINT MINING OF CENTRAL F.UROPEof chief siliceous rocks, mincs and probable min es in Central Europę
FLINT MINING OF CENTRAL EUROPE 55 Rook E. 1963 Materiały z jaskini Bęblowskiej Dolnej, „Materiały
FLINT MINING OF CENTRAL F.UROPE 33 5. UNDERGROUND SHAFTS WITH NICHES Underground shafts with niche w
FLINT MINING OF CENTRAL HUROPE 37 tion as a result of connccting the workings of three ad-jacent sha
FLINT MINING OF CLNTRAL EUROPE 47 mon cultural tradition. Many years ago, J. K. Kozłowski showed tha
więcej podobnych podstron