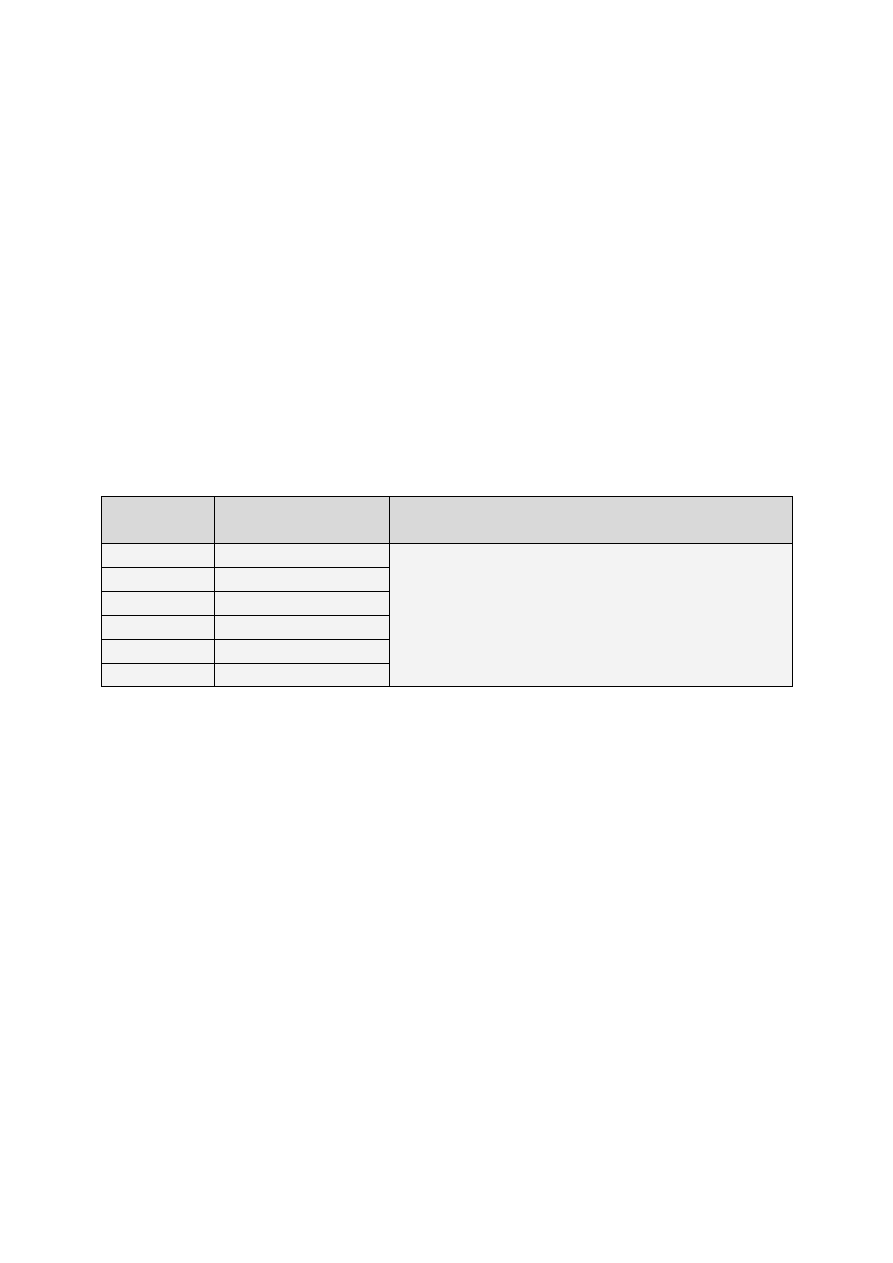
Past Perfect
Czas zaprzeszły
I. Form
Tworzenie czasu
Positive
Forma twierdząca
When I arrived at the party, the president had gone.
He wasn’t hungry, he had had a meal.
My room was filthy, I had cleaned it a few weeks before.
Full form
Forma pełna
Contracted form
Forma ściągnięta
Past participle
Imiesłów czasu przeszłego
I had
I’d
gone
had
cleaned
done
been
brought
you had
you’d
he, she, it had
he’d, she’d
we had
we’d
you had
you’d
they had
they’d
Remember
Zapamiętaj
had + past participle
had + imiesłów czasu przeszłego
The past participle form is the same as for present perfect.
Forma imiesłowu czasu przeszłego tworzona jest taka sama jak dla czasu teraźniejszego dokonanego.
Negative
Forma przecząca
I was afraid because I had not flown before.
We were so happy to meet them because we hadn’t seen each other for ages.
The negative form of both regular and irregular verbs is formed with had not (or hadn’t) and the past
participle.
Forma przecząca czasowników regularnych i nieregularnych tworzona jest za pomocą operatora had
not (lub hadn’t) i imiesłowu czasu przeszłego.
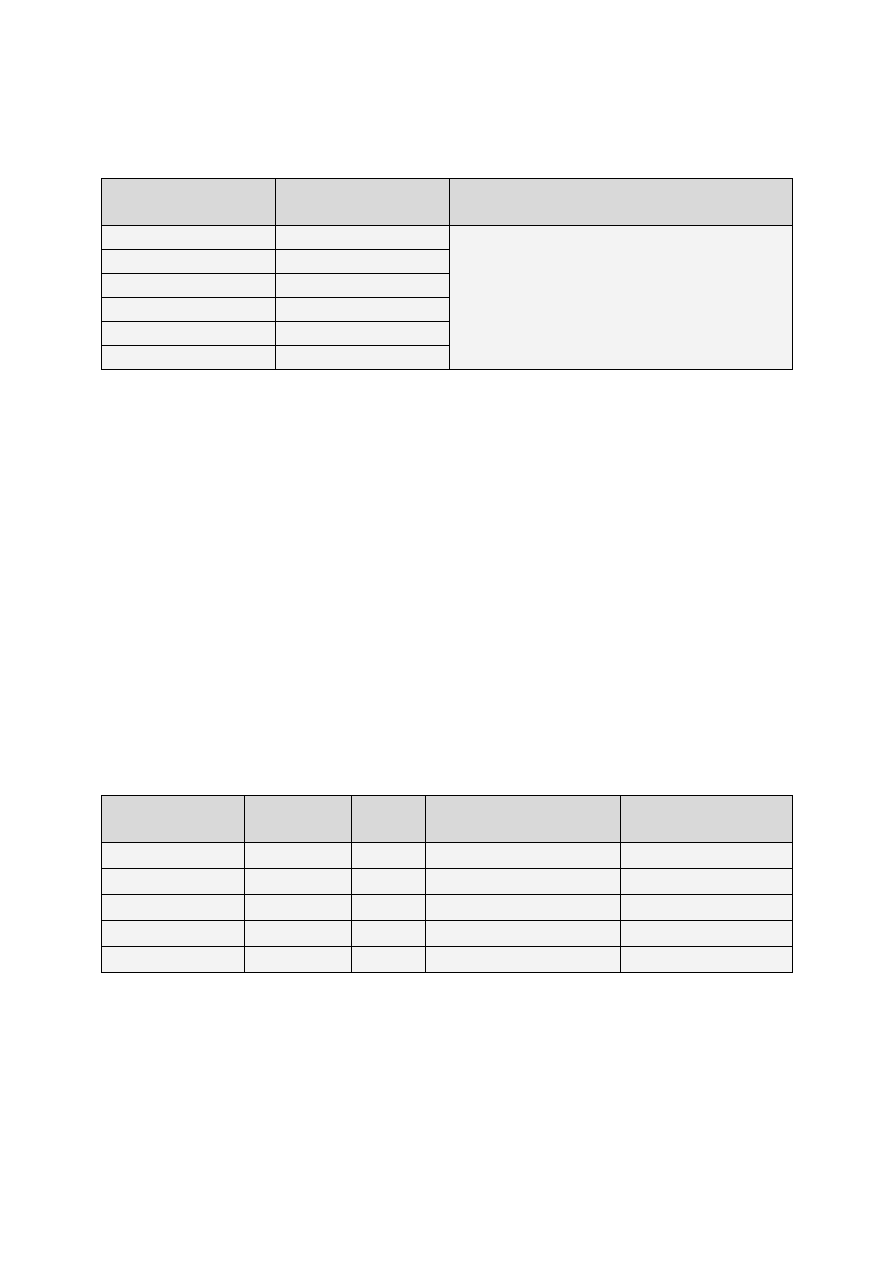
Full form
Forma pełna
Contracted form
Forma ściągnięta
Past participle
Imiesłów czasu przeszłego
I had not
I hadn’t
cleaned
finished
lost
done
been
brought
you had not
you hadn’t
he, she, it had not
he, she, it hadn’t
we had not
we hadn’t
you had not
you hadn’t
they had not
they hadn’t
Remember
Zapamiętaj
had + not + past participle
had + not + imiesłów czasu przeszłego
Questions
Forma pytająca
Had Paul gone home when you arrived?
What had he done that the police arrested him?
Where had you been that your shoes were so dirty?
To make questions, we use the same auxiliary verb and change the word order in the sentence.
Do tworzenia pytao używamy tego samego operatora I zmieniamy kolejność wyrazów w zdaniu.
Question word
Zaimek pytający
Auxiliary verb
Operator
Subject
Podmiot
Past Participle
Imiesłów czasu przeszłego
Had
Paul
gone
home?
Had
she
been
to Spain?
Had
you
seen
anything interesting?
Where
had
you
been?
What
had
he
done?
Remember
Zapamiętaj
had + subject + past participle
had + podmiot + imiesłów czasu przeszłego
or
lub
had + subject + past participle
had + podmiot + imiesłów czasu przeszłego
Short answers
Krótka odpowiedź
„Had you been to London before?” “Yes, I had.”
Yes, I, you, we, they had.
No, I, you, we, they hadn’t.
Yes, he, she, it had.
No, he, she, it hadn’t.
II. Use
Użycie czasu
The past perfect tense is said used to talk about the events which took place before the starting point
of the story.
Czas zaprzeszły jest używany do mówienia o wydarzeniach, które nastąpiły przed początkiem
opowiadania.
When I got home, I realized that a thief had broken into.
I tried to get in touch with her this morning, but she had gone abroad.
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Czas zaprzeszły
Czas zaprzeszły
Czas zaprzeszły Pretérito pluscuamperfecto de Indicativo, Języki obce, Język hiszpański, Gramatyka
Pretérito Anterior Czas zaprzeszły
Czas zaprzeszły das Plusquamperfekt
Czas zaprzeszły
Czas zaprzeszly, ✔ GRAMATYKA W OPISIE OD A DO Z
Czas zaprzeszły
Czas zaprzeszły
Czas zaprzeszły
Czas zaprzeszly
Czas zaprzeszły w polskiej fleksji
CZAS ZAPRZESZLY
Czas zaprzeszły
37 plusquamperfekt czas zaprzeszy
CZAS WOLNY(1)
Czas w kulturze ped czasu wolnego
więcej podobnych podstron