netter166
|
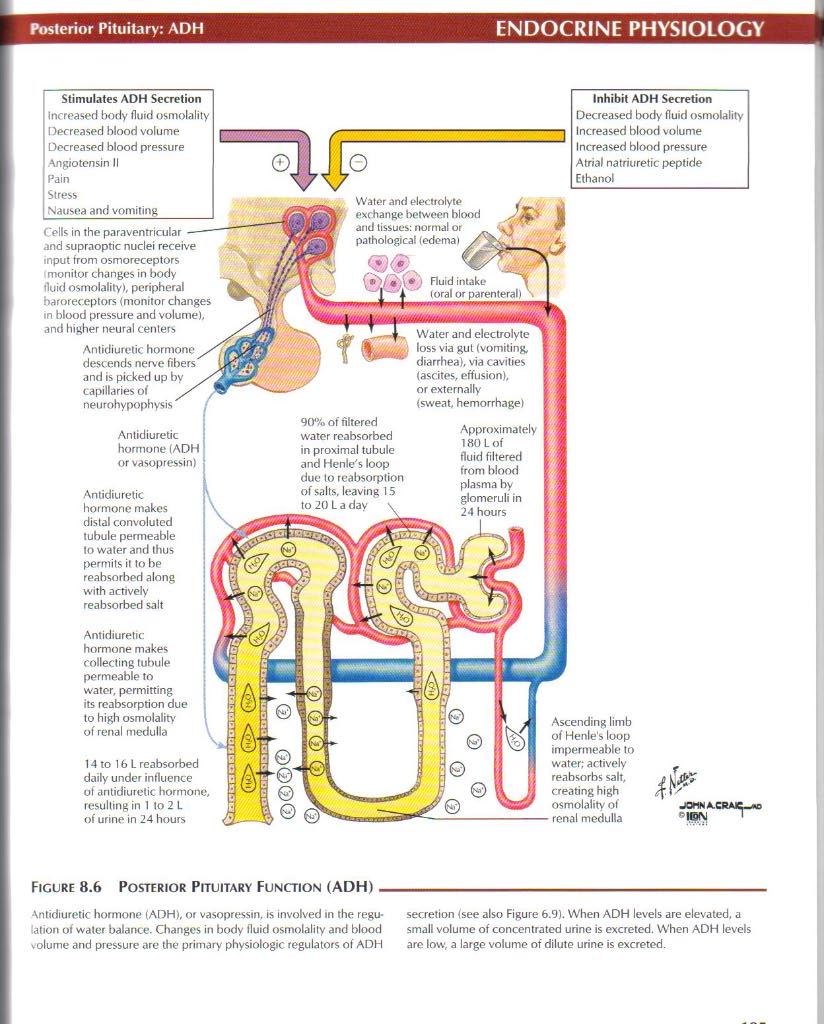
Stimulates ADH Secretion Increased body fluid osmolality | |
|
Decreased blood volume Decreased blood pressure Angiotensin II Pain Stress Nausea and vomiting | |
|
©1 | |
|
Cells in the paraventricular--"" ' | |
Inhibit ADH Secretion
Decreased body fluid osmolality Increased blood volume Increased blood pressure Atrial natriuretic peptide Ethanol
and supraoptic nuclei receive input from osmoreceptors monitor changes in body fluid osmolality), pcripheral baroreceptors (monitor changes in blood pressure and vołume), and higher neural centers
Antidiurelic hormone descends nerve fibers and is picked up by capillaries o i neurohypophysi;
Antidiurelic hormone (ADH or vasopressin)
Antidiuretic hormone makes distal convoluted tubule permeable to water and thus permits it to be reahsorbed along with actively reabsorbed salt
Antidiuretic hormone makes collecting tubule permeable to water, permitting its reabsorption due to high osmolality of renal medulla
14 to 16 L reabsorbed daily under influence of antidiurelic hormone, resulling in 1 to 2 L of urine in 24 hours
Water and electrolyte exchange between blood and tissues: normal or pathological (edemal
Fluid intake ^ (orał or parenteral)
Water and electrolyte loss via gul (vomiting, diarrhea), via cavities (ascites, effusion), or extemally (sweat, hemorrhage)
90% of filtered water reabsorbed in proximal tubule and Henle's loop due to reabsorption of salts, leaving 15 to 20 L a day \
Approximately
180 Lof fluid filtered from blood
; .I i-m i In
glomeruli i 24 hours
Ascending limb
of Henles loop
impermeable to
water; actively
re.ihsorhs sali.
c reating high
( IMT1( If.)111\ Ul
JOHNAOtNBMlB
IBM
Figurę 8.6 Posterior Pituitary Function (ADH)-
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), or vasopressin, is involved in the regu- secretion (see also Figurę 6.9). When ADH levels are elevated, a lation of water balance. Changes in body fluid osmolality and blood smali volume of concentrated urine is excreted. When ADH leve!s volume and pressure are the primary physiologic regulators of ADH are Iow, a large volume of dilute urine is excreted.
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
55386 netter164 Anterior PituitaryENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY endocrine glands. The hormones secreted by th
netter109 Renal Clearance: IIRENAL PHYSIOLOGY PRINCIPIE OF TUBULAR SECRETION LIMITATION (Tm) USINC P
16523 netter73 Rrsponse to txeras»CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Anticipation of exercise stimulates
netter73 Rrsponse to txeras»CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Anticipation of exercise stimulates
16523 netter73 Rrsponse to txeras»CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Anticipation of exercise stimulates
netter141 Smali Intestine MotiiityGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Rhythmic sepmentation Intraluminal
netter152 Intrahepatii Biliary SystemGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Noto. The figurę shows bile canalic
netter172 Adrenai Cland: HistologyENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Capsule Zona glomerulosa Capsular plexus Caps
netter180 Actions of InsulinENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 8.20 Actions of Insulin- Insulin is a fueł-s
netter190 Whcn words alone won t do, think NetterNetter s Atlas of Humań PhysiologyJohn T. Hansen, P
netter49 I I Cardiac Mustlt*: StructureMUSCLE PHYSIOLOGYFlCURF 3.7 SCHEMA OF STRUCFURt OF CARDIAC MU
netter52 Fxcitation-Conlraclion CouplingMUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY HART 3.1 COMPARISION OF MUSCLE STRUCTURE A
netter78 Airway Structure: EpithcliumRESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Mucus- Goblet (mucous)
netter93 O, and CO_. ExchangrRESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 5.19 02 and CO, Exchange As blood flows I
więcej podobnych podstron