51416 netter101
Restrictive Lung Dise
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY
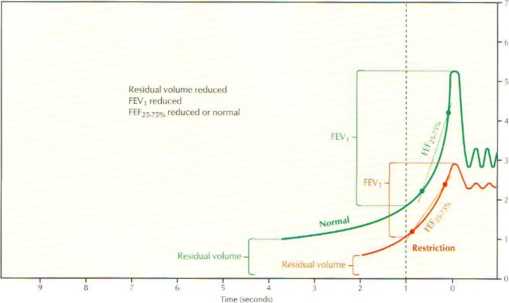
Maximum Expiratory riow-Volume Curves
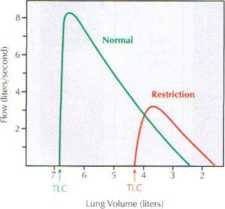
Total Lung _ Capacity (TLC)
TI.C and VC deoeased
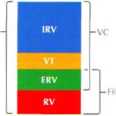
Restriction
Normal
J. Perkins
MS. MFA
*MDM
Figurę 5.27 Restrictive Pulmonary Disease
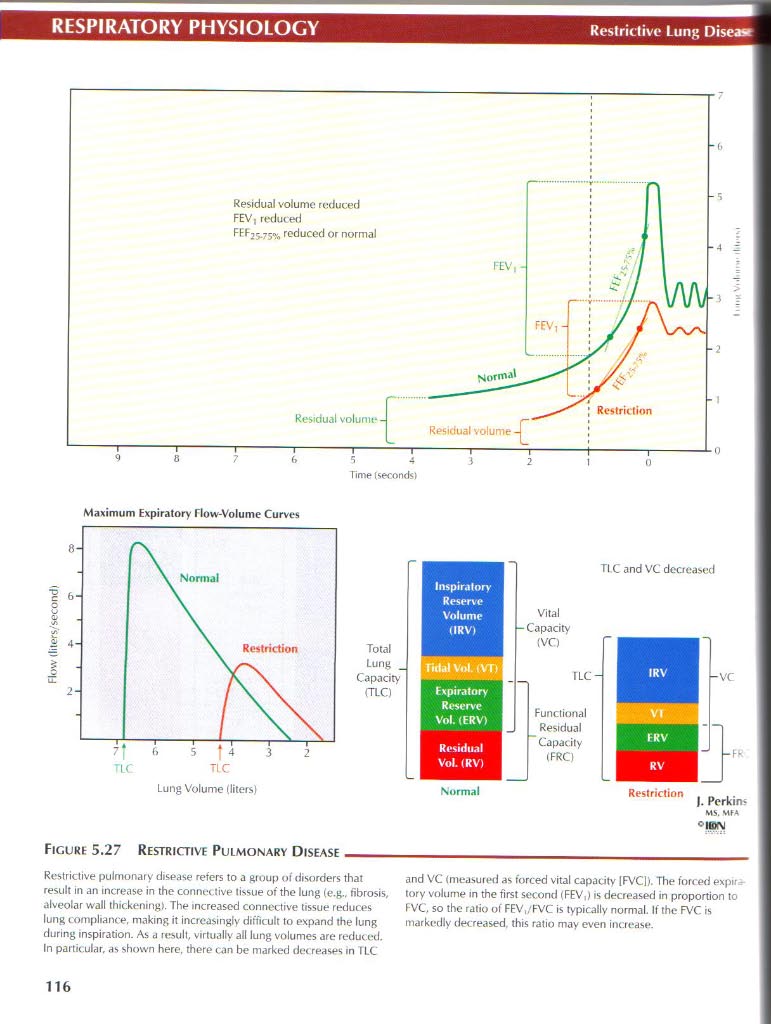
Rcstrictive pulmonary disease refers to a group of disorders that result in an increase in the connective tissue ot the lung (e.g.. fibrosis, alveolar wali thickening). The increasod connective tissue red u ces lung compliance, making it incrcasingly difflcult to expand the lung during inspiration. As a result, virtually all lung volumes are reduced. In particular, as shown herc. thore can be marked decreases in TLC and VC (measured as torced vital capacity 1F\/C1>. The forced expir tory volume in the first second <FEV,> is decrcased in proportion to FVC, so the ratio of FEV,/FVC is typically normal. If the FVC is markcdly decreased. this ratio may even increase.
116
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
23704 netter100 JłKtructiye Lung DiseaseRESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Masimum Expiratorv Flow-Volume Curves
68548 netter99 Obstructive Lung DiseaseRESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Centriacinar (Ccntrilobular) Emphyscma
netter109 Renal Clearance: IIRENAL PHYSIOLOGY PRINCIPIE OF TUBULAR SECRETION LIMITATION (Tm) USINC P
netter135 Gastric Secretion: IGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Neurocrine Regulalion of Acid
netter136 Gaslric Secretion: IIGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Secrelions of gastric acid (H* ) by parie
netter141 Smali Intestine MotiiityGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Rhythmic sepmentation Intraluminal
netter152 Intrahepatii Biliary SystemGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Noto. The figurę shows bile canalic
netter163 Hypothalamus and PituitaryENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Ihalamus Hypothalamic sulcus Hypothalamic a
netter172 Adrenai Cland: HistologyENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Capsule Zona glomerulosa Capsular plexus Caps
netter180 Actions of InsulinENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 8.20 Actions of Insulin- Insulin is a fueł-s
netter190 Whcn words alone won t do, think NetterNetter s Atlas of Humań PhysiologyJohn T. Hansen, P
netter49 I I Cardiac Mustlt*: StructureMUSCLE PHYSIOLOGYFlCURF 3.7 SCHEMA OF STRUCFURt OF CARDIAC MU
netter52 Fxcitation-Conlraclion CouplingMUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY HART 3.1 COMPARISION OF MUSCLE STRUCTURE A
netter78 Airway Structure: EpithcliumRESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Mucus- Goblet (mucous)
netter93 O, and CO_. ExchangrRESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 5.19 02 and CO, Exchange As blood flows I
16523 netter73 Rrsponse to txeras»CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Anticipation of exercise stimulates
więcej podobnych podstron