Measuring
Measuring
competitiveness: methods
competitiveness: methods
and indicators
and indicators
What
What
is
is
Competitiveness
Competitiveness
?
?
-
-
Michael
Michael
Porter’s
Porter’s
definition
definition
•
•
Competitiveness
Competitiveness
is
is
determined
determined
by
by
the
the
productivity
productivity
with
with
which
which
a
a
nation
nation
uses
uses
its
its
human
human
,
,
capital
capital
,
,
and
and
natural
natural
resources
resources
.
.
•
•
Nations
Nations
compete
compete
in
in
offering
offering
the
the
most
most
productive
productive
environment for business
environment for business
Determinants of
Determinants of
p
p
roductivity
roductivity
and
and
p
p
roductivity
roductivity
g
g
rowth
rowth
•
•
Macroeconomic, political, legal, and social
Macroeconomic, political, legal, and social
conditions for development
conditions for development
•
•
Microeconomic conditions of development
Microeconomic conditions of development
(quality of
(quality of
busin
busin
e
e
ss
ss
environment; sophistication
environment; sophistication
of local companies; competition)
of local companies; competition)
Porter’s Diamond
Porter’s Diamond
4 determinants
4 determinants
of a nation’s competitive advantage
of a nation’s competitive advantage
relative to other countries
relative to other countries
1.
1.
Demand conditions
Demand conditions
2.
2.
Factor conditions
Factor conditions
3.
3.
Related and supporting industries
Related and supporting industries
4.
4.
Company strategy, structure, rivalry
Company strategy, structure, rivalry
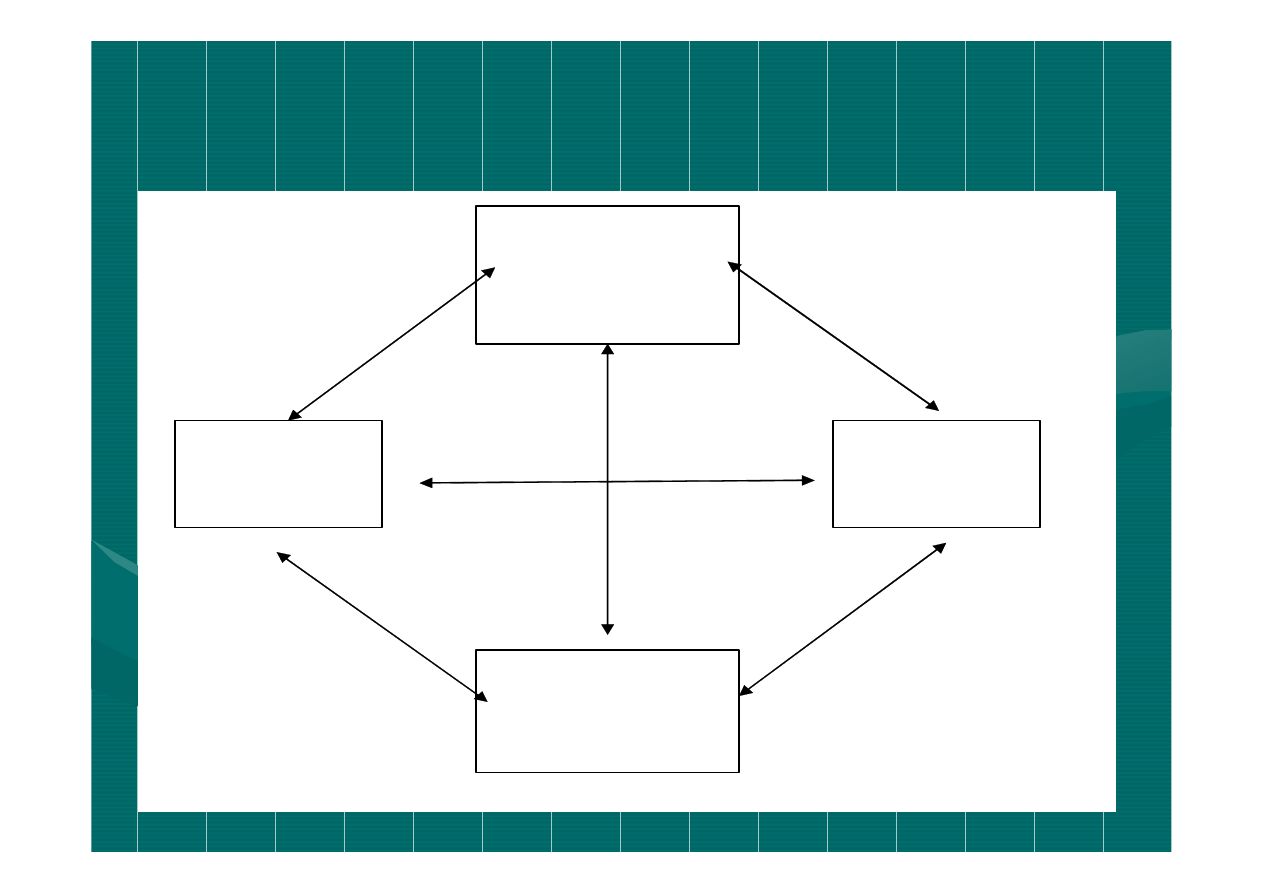
Porter’s Diamond
Porter’s Diamond
F ir m str a te g y ,
str u c tu r e , a n d
r iv a lr y
R e la te d a n d
su p p o r tin g
in d u str ie s
D e m a n d
c o n d itio n s
F a c to r
c o n d itio n s
Źródło: M. Porter , 2001.
Demand conditions
Demand conditions
•
•
Home market, size of demand, its
Home market, size of demand, its
sophistications etc…
sophistications etc…
•
•
Public procurement rules
Public procurement rules
Factor conditions
Factor conditions
•
•
Availability of resources and skills: natural
Availability of resources and skills: natural
resources, physical capital, human c
resources, physical capital, human c
a
a
pital
pital
,
,
infrastructure, etc.
infrastructure, etc.
Related and supporting industries
Related and supporting industries
•
•
Suppliers
Suppliers
•
•
Related industries
Related industries
•
•
Subcontractors
Subcontractors
•
•
Existence of clusters
Existence of clusters
Company strategy, structure, rivalry
Company strategy, structure, rivalry
•
•
Market structure
Market structure
•
•
Labor market rules
Labor market rules
•
•
Corruption level
Corruption level
•
•
Barriers for businesses
Barriers for businesses
•
•
Bureaucracy
Bureaucracy
The ‘diamond’ as a system
The ‘diamond’ as a system
•
•
One element of diamond often depends on
One element of diamond often depends on
others (
others (
eg
eg
. human resources and sophistication
. human resources and sophistication
of demand)
of demand)
•
•
One element can reinforce others (
One element can reinforce others (
eg
eg
.
.
competition rules influence factor conditions)
competition rules influence factor conditions)
The most important factors that
The most important factors that
determine competitiveness of the
determine competitiveness of the
economies
economies
•
•
Posses
Posses
s
s
ed and created assets
ed and created assets
-
-
their structure and
their structure and
quality
quality
•
•
Institutions and policies (intangibles) and their
Institutions and policies (intangibles) and their
quality
quality
•
•
Usage of tangibles and intangibles and its
Usage of tangibles and intangibles and its
efficiency
efficiency
Assets, their structure and quality
Assets, their structure and quality
•
•
Natural resources (energy and mineral resources), cultivable lan
Natural resources (energy and mineral resources), cultivable lan
d,
d,
size and structure of water supply, climate conditions
size and structure of water supply, climate conditions
•
•
Technical infrastructure (transport, energy, water
Technical infrastructure (transport, energy, water
-
-
supply)
supply)
•
•
Social infrastructure (education and health
Social infrastructure (education and health
-
-
care system)
care system)
•
•
Human resources (employed foreigners included)
Human resources (employed foreigners included)
-
-
number, age
number, age
structure of the human resources
structure of the human resources
•
•
Capital resources
Capital resources
-
-
production capital and financial capital
production capital and financial capital
(foreign capital included)
(foreign capital included)
•
•
Level of technology (technology of production,
Level of technology (technology of production,
manag
manag
e
e
ment
ment
,
,
marketing, finances and so on including import of the
marketing, finances and so on including import of the
technology)
technology)
I
I
nstitutions
nstitutions
and policies and their
and policies and their
quality
quality
•
•
Creativity and innovation
Creativity and innovation
–
–
the ability to create
the ability to create
new solutions and to implement them
new solutions and to implement them
•
•
Entrepreneurship and willingness to take risk
Entrepreneurship and willingness to take risk
•
•
The level of institutional development and its
The level of institutional development and its
efficiency (including conditions for business
efficiency (including conditions for business
sector)
sector)
•
•
Economic policy and its efficiency
Economic policy and its efficiency
•
•
Human capital
Human capital
Efficiency
Efficiency
of
of
making
making
use
use
of
of
assets
assets
and
and
institutions
institutions
•
•
Efficiency
Efficiency
=
=
value
value
created
created
per
per
the
the
labour
labour
or
or
capital
capital
unit
unit
How can you measure competitiveness
How can you measure competitiveness
of a country in a global economy?
of a country in a global economy?
•
•
?????
?????
Measures of competitiveness should
Measures of competitiveness should
satisfy 3 basic criteria:
satisfy 3 basic criteria:
1.
1.
cover all the sectors exposed to competition,
cover all the sectors exposed to competition,
2.
2.
encompass all the markets open to
encompass all the markets open to
competition,
competition,
3.
3.
can be calculated using data that are fully
can be calculated using data that are fully
comparable internationally
comparable internationally
Measurment
Measurment
: quantity and quality
: quantity and quality
•
•
For competitiveness,
For competitiveness,
quality
quality
is more important
is more important
than quantity
than quantity
as t
as t
he quality of the market and
he quality of the market and
production, in connection with technical
production, in connection with technical
progress, determine the country’s economic
progress, determine the country’s economic
power in the long run
power in the long run
•
•
This qualitative aspect boils down to three
This qualitative aspect boils down to three
abilities of every country:
abilities of every country:
a) accumulation ability,
a) accumulation ability,
b) investment ability,
b) investment ability,
c) management ability
c) management ability
Other
Other
important
important
factors
factors
•
•
structure and influence of the external “political
structure and influence of the external “political
climate”
climate”
•
•
changes in international economic policy
changes in international economic policy
•
•
changes in other countries’ capacity and abilities
changes in other countries’ capacity and abilities
to compete.
to compete.
M
M
easurement
easurement
of these factors is
of these factors is
difficul
difficul
t,
t,
therefore
therefore
there
there
are
are
attempts to measure specific internal
attempts to measure specific internal
factors (advantages) and
factors (advantages) and
(r
(r
ather
ather
rarely
rarely
)
)
external
external
factors
factors
.
.
M
M
easures
easures
•
•
can be initially divided according to various
can be initially divided according to various
criteria:
criteria:
a) period under analysis;
a) period under analysis;
b) manner of measurement;
b) manner of measurement;
c) level and scope of statistical data aggregation.
c) level and scope of statistical data aggregation.
C
C
omposite
omposite
measures and methods to measure
measures and methods to measure
international competitive ability
international competitive ability
T
T
here are
here are
:
:
•
•
measures of “the magic quadrangle”
measures of “the magic quadrangle”
•
•
”
”
magic
magic
pentagon”
pentagon”
•
•
indices of economic freedom
indices of economic freedom
T
T
he magic quadrangle and magic
he magic quadrangle and magic
pentagon methods
pentagon methods
•
•
Based
Based
on
on
the main indicators of
the main indicators of
macroeconomic stabilization, i.e.
macroeconomic stabilization, i.e.
:
:
1.
1.
rate of growth
rate of growth
(GDP
(GDP
growth
growth
)
)
,
,
2.
2.
unemployment,
unemployment,
3.
3.
inflation,
inflation,
4.
4.
share of state budget deficit or surplus in GDP
share of state budget deficit or surplus in GDP
5.
5.
share of the current
share of the current
-
-
account deficit or surplus
account deficit or surplus
in GDP
in GDP
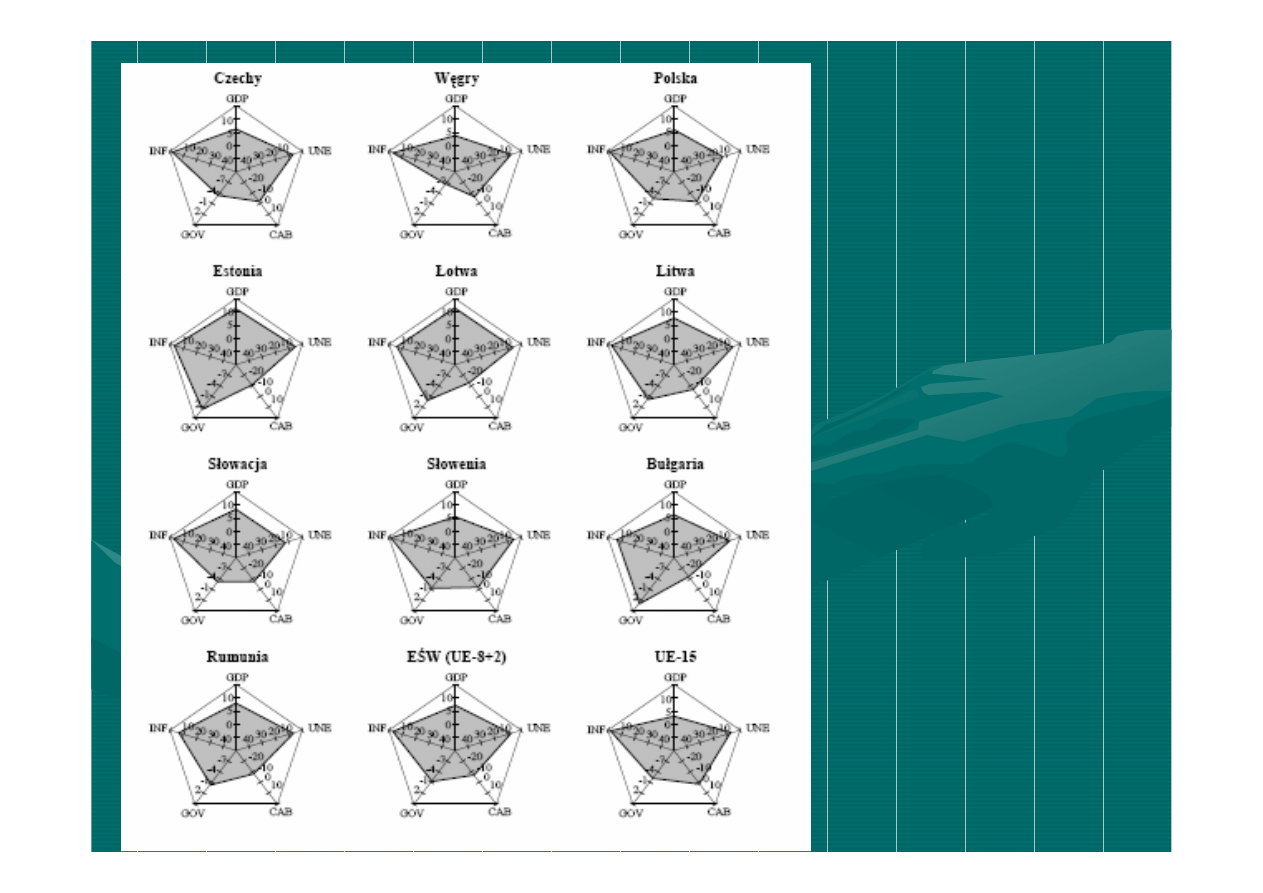
„
„
Magic
Magic
pentagon
pentagon
in
in
practice
practice
GDP–
growth rate (%)
INF–
inflation (%)
UNE–
unemployment (%)
GOV–
government
debt/surplus (in % GDP)
CAB–
current account
deficit/surplus (
in % GDP)
Magic
Magic
pentagon
pentagon
-
-
main
main
drawbacks
drawbacks
•
•
Existence of economic tradeoffs between
Existence of economic tradeoffs between
different macroeconomic policy aims
different macroeconomic policy aims
,
,
which
which
lead to lack of optimization;
lead to lack of optimization;
•
•
d
d
ifficulties
ifficulties
with direct comparisons, weighing
with direct comparisons, weighing
and ranking of separate segment indices;
and ranking of separate segment indices;
possibility of one
possibility of one
-
-
side segment indices (e.g. due
side segment indices (e.g. due
to twin deficits);
to twin deficits);
•
•
d
d
ifficulties
ifficulties
of international comparisons over
of international comparisons over
time
time
Indices of economic freedom
Indices of economic freedom
•
•
I
I
n order to assess the degree of economic freedom the
n order to assess the degree of economic freedom the
following elements are evaluated:
following elements are evaluated:
a/ Economic policy;
a/ Economic policy;
b/ Tax policy;
b/ Tax policy;
c/ Consumption and production development;
c/ Consumption and production development;
d/ Flows of FDI;
d/ Flows of FDI;
e/ Degree of banking system development;
e/ Degree of banking system development;
f/ Price and wage controls;
f/ Price and wage controls;
g/ Stand of property rights;
g/ Stand of property rights;
h/ Market entry and exit barriers;
h/ Market entry and exit barriers;
i/ Scale and scope of the shadow economy and black markets
i/ Scale and scope of the shadow economy and black markets
Indices of economic freedom
Indices of economic freedom
Basic drawbacks
Basic drawbacks
:
:
•
•
relatively weak theoretical foundations;
relatively weak theoretical foundations;
•
•
arbitrary and selectable choice of selected indices as well
arbitrary and selectable choice of selected indices as well
as their arbitrary evaluation and assessment;
as their arbitrary evaluation and assessment;
•
•
ranking difficulties with regard to segment (fragmentary)
ranking difficulties with regard to segment (fragmentary)
measures;
measures;
•
•
difficulties of international comparisons with time passage
difficulties of international comparisons with time passage
Methods of measuring international
Methods of measuring international
competitiveness
competitiveness
Key measures of international price
Key measures of international price
competitiveness
competitiveness
:
:
•
•
Unit values
Unit values
•
•
Relative prices in imports and exports
Relative prices in imports and exports
•
•
Real exchange rates
Real exchange rates
•
•
Terms of trade
Terms of trade
Selected measures of international competitive
Selected measures of international competitive
position
position
•
•
Shares in international trade
Shares in international trade
•
•
Trade balance
Trade balance
•
•
Import penetration indicators (“ability to
Import penetration indicators (“ability to
compete” indicators)
compete” indicators)
•
•
Imports
Imports
-
-
Exports ratios and indicator of
Exports ratios and indicator of
exports specialization
exports specialization
Selected measures of international competitive
Selected measures of international competitive
position
position
Methods of measurement
Methods of measurement
:
:
•
•
Revealed Comparative Advantages
Revealed Comparative Advantages
methodology (RCA)
methodology (RCA)
•
•
Intra
Intra
-
-
industry trade analyses (IIT)
industry trade analyses (IIT)
•
•
Constant Market Share analyses (CMS)
Constant Market Share analyses (CMS)
•
•
Price ratios algorithm (PRA)
Price ratios algorithm (PRA)
Measures of the international competitive position of
Measures of the international competitive position of
countries
countries
with regard to their attractiveness to internationally mobile
with regard to their attractiveness to internationally mobile
production
production
factors
factors
:
:
•
•
Shares in international movements of basic
Shares in international movements of basic
production factors (labor, capital,
production factors (labor, capital,
technology)
technology)
•
•
Balance of foreign direct investment, in
Balance of foreign direct investment, in
absolute and/or relative terms (e.g. in
absolute and/or relative terms (e.g. in
relation to GDP)
relation to GDP)
•
•
Balance of total capital flows of the
Balance of total capital flows of the
analyzed countries
analyzed countries
Measuring export competitiveness:
Measuring export competitiveness:
RCA index
RCA index
RCA (
RCA (
R
R
evealed
evealed
C
C
omparative
omparative
A
A
dvantage) is defined as follows:
dvantage) is defined as follows:
RCA i=
RCA i=
ln
ln
[(
[(
Xij
Xij
/
/
Mij
Mij
) : (
) : (
Xj
Xj
/
/
Mj
Mj
] ,
] ,
•
•
where
where
Xij
Xij
is export of commodity i by country j ,
is export of commodity i by country j ,
•
•
Mij
Mij
is import of commodity i by country j
is import of commodity i by country j
•
•
Xj
Xj
and
and
Mj
Mj
are total country’s j exports and imports.
are total country’s j exports and imports.
RCA
RCA
i
i
indicators range from
indicators range from
-
-
∞
∞
to +
to +
∞
∞
An
An
RCAi
RCAi
above zero points to a revealed comparative
above zero points to a revealed comparative
advantage; the reverse is true of indicators below zero
advantage; the reverse is true of indicators below zero
Conclusion
Conclusion
:
:
When RCA>0 a country is relatively
When RCA>0 a country is relatively
speciali
speciali
z
z
ed in this
ed in this
group of goods.
group of goods.
Measures of technological competitiveness
Measures of technological competitiveness
•
•
Shares in international flows of embodied and
Shares in international flows of embodied and
disembodied technology
disembodied technology
•
•
Balance of trade with regard to embodied and
Balance of trade with regard to embodied and
disembodied technology
disembodied technology
•
•
Expenditures on R&D, nominal or relative (e.g.
Expenditures on R&D, nominal or relative (e.g.
as a percentage of GDP)
as a percentage of GDP)
•
•
Absolute and relative volume or value of
Absolute and relative volume or value of
registered patents, sold licenses etc.
registered patents, sold licenses etc.
•
•
Method of subtracting technology productivity
Method of subtracting technology productivity
(TP) from indices of total factor productivity
(TP) from indices of total factor productivity
(TFP)
(TFP)
The
The
most
most
important
important
factors
factors
of
of
countries
countries
’
’
competitiveness
competitiveness
and
and
ways
ways
of
of
measuring
measuring
:
:
ASSETS
ASSETS
Country
Country
’
’
s
s
share
share
in
in
the
the
global
global
resources
resources
(
(
chosen
chosen
resources
resources
,
,
clasified
clasified
as
as
strategic
strategic
by J.
by J.
Dunning
Dunning
-
-
eg.
eg.
oil
oil
,
,
gas
gas
,
,
copper
copper
,
,
nickel
nickel
)
)
Natural
Natural
resources
resources
(
(
energy
energy
and
and
mineral
mineral
resources
resources
),
),
cultivable
cultivable
land,
land,
size
size
and
and
structure
structure
of
of
water
water
supply
supply
,
,
climate
climate
conditions
conditions
Basic
Basic
measures
measures
Determinants
Determinants
The
The
most
most
important
important
factors
factors
of
of
countries
countries
’
’
competitiveness
competitiveness
and
and
ways
ways
of
of
measuring
measuring
:
:
ASSETS
ASSETS
1.
1.
Density
Density
of
of
:
:
-
-
road
road
network
network
(for 100 km2)
(for 100 km2)
-
-
rail
rail
network
network
, etc
, etc
…
…
Technical
Technical
infrastructure
infrastructure
(transport,
(transport,
energy
energy
,
,
water
water
-
-
supply
supply
)
)
Basic
Basic
measures
measures
Determinants
Determinants
The
The
most
most
important
important
factors
factors
of
of
countries
countries
’
’
competitiveness
competitiveness
and
and
ways
ways
of
of
measuring
measuring
:
:
ASSETS
ASSETS
1.
1.
School attainment
School attainment
ratio
ratio
2.
2.
Infant mortality
Infant mortality
Social
Social
infrastructure
infrastructure
(
(
education
education
and
and
health
health
-
-
care
care
system)
system)
Basic
Basic
measures
measures
Determinants
Determinants
The
The
most
most
important
important
factors
factors
of
of
countries
countries
’
’
competitiveness
competitiveness
and
and
ways
ways
of
of
measuring
measuring
:
:
ASSETS
ASSETS
1.
1.
Cost of
Cost of
labour
labour
2.
2.
Share of highly educated people in
Share of highly educated people in
the number of employees
the number of employees
3.
3.
Graduates
on
engineers
Graduates
on
engineers
’
’
and
and
technical majors as a percentage of
technical majors as a percentage of
20
20
-
-
29 years old people
29 years old people
Human
Human
resources
resources
(
(
employed
employed
foreigners
foreigners
included
included
)
)
-
-
number
number
,
,
age
age
structure
structure
,
,
quality
quality
of
of
the
the
human
human
resources(level
resources(level
of
of
education
education
)
)
Basic
Basic
measures
measures
Determinants
Determinants
The
The
most
most
important
important
factors
factors
of
of
countries
countries
’
’
competitiveness
competitiveness
and
and
ways
ways
of
of
measuring
measuring
:
:
INSTITUTIONS AND POLICIES
INSTITUTIONS AND POLICIES
1.
1.
Corruption
Corruption
rate
rate
eg.
eg.
according
according
to
to
Transparency
Transparency
International
International
The
The
level
level
of
of
institutional
institutional
development
development
and
and
its
its
efficiency
efficiency
1.
1.
Number
Number
of
of
newly
newly
established
established
private
private
companies
companies
in
in
relation
relation
to
to
closed
closed
companies
companies
Tendency
Tendency
to
to
enterprise
enterprise
and
and
taking
taking
risk
risk
1.
1.
Intensity
Intensity
of
of
innovations
innovations
(
(
expenses
expenses
for
for
innovations
innovations
as a
as a
percentage
percentage
of
of
sales
sales
)
)
2.
2.
Number
Number
of
of
publications
publications
for 1
for 1
mln
mln
of
of
population
population
Creativity
Creativity
and
and
innovation
innovation
–
–
the
the
ability
ability
to
to
create
create
new
new
solutions
solutions
and
and
to
to
implement
implement
them
them
Basic
Basic
measures
measures
Determinants
Determinants
The
The
most
most
important
important
factors
factors
of
of
countries
countries
’
’
competitiveness
competitiveness
and
and
ways
ways
of
of
measuring
measuring
:
:
INSTITUTIONS AND POLICIES
INSTITUTIONS AND POLICIES
Number
Number
of
of
associations
associations
(
(
excluding
excluding
labour
labour
unions
unions
and
and
religious
religious
organizations
organizations
)
)
according
according
to
to
number
number
of
of
inhabitants
inhabitants
Human
Human
and
and
cultural
cultural
capital
capital
Economic
Economic
liberalization
liberalization
rate
rate
eg.
eg.
according
according
to
to
Heritage
Heritage
Foundation
Foundation
1
1
Economic
Economic
policy
policy
and
and
its
its
efficiency
efficiency
Basic
Basic
measures
measures
Determinants
Determinants
The
The
most
most
important
important
factors
factors
of
of
countries
countries
’
’
competitiveness
competitiveness
and
and
ways
ways
of
of
measuring
measuring
:
:
efficiency
efficiency
Value
Value
added
added
for
for
labour
labour
and
and
capital
capital
unit
unit
Productivity
Productivity
of
of
labour
labour
and
and
capital
capital
Basic
Basic
measures
measures
Determinants
Determinants
R
R
eports
eports
assessing
assessing
international
international
competitiveness
competitiveness
Issued
Issued
by:
by:
•
•
the International Institute for Management
the International Institute for Management
Development
Development
(IMD)
(IMD)
,
,
•
•
the World Economic Forum
the World Economic Forum
(WEF)
(WEF)
•
•
the Bertelsmann Foundation
the Bertelsmann Foundation
They contain many different measures and
They contain many different measures and
evaluations of the strengths and weaknesses
evaluations of the strengths and weaknesses
of various countries.
of various countries.

Competitiveness
Competitiveness
rankings
rankings
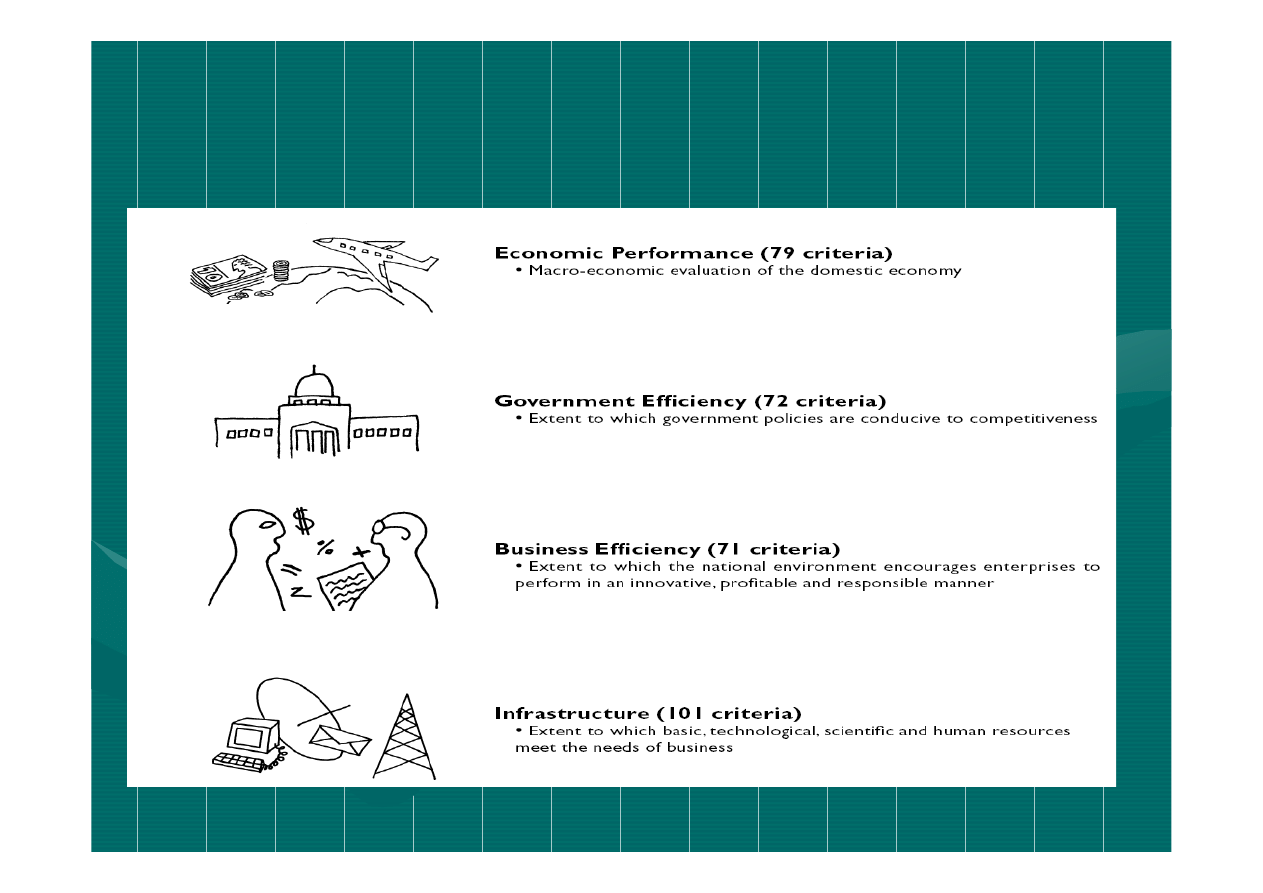
WCY– annual report about
competitiveness issued by
IMD in
Lozanna from 1989 r.
Evaluation of the economies of 55
countries based on 323 criteria
mesuring different competitiveness
factors: 2/3 of the data- statistical
data (national and international
sources), 1/3 -Executive Opinion
Survey
http://www.imd.ch/research/challenges/TC043-07.cfm
Competitiveness
Competitiveness
rankings
rankings
-
-
WCY
WCY
Źródłó: IMD WCY 2007

Competitiveness
Competitiveness
rankings
rankings
WEF Global Competitiveness Report –
annual report about
competitiveness
issued by
WEF from 1979 r.
Evaluation of the economies of 131
countries based on statistical data and
surveys- 12 pillars of
competitiveness
http://www.gcr.weforum.org/
Definition according to WEF:
We define
competitiveness
as
the set of institutions, policies, and factors
that determine the level of productivity of a country
. (WEF, 2007, p. 3)
Evaluation
Evaluation
of
of
competitiveness
competitiveness
-
-
WEF
WEF
•
•
From
From
2004 r.:
2004 r.:
The
The
Global
Global
Competitiveness
Competitiveness
Report
Report
contains
contains
Global
Global
Competitiveness
Competitiveness
Index
Index
and
and
Business
Business
Competitiveness
Competitiveness
Index
Index
•
•
Authors
Authors
of
of
the
the
indexes
indexes
:
:
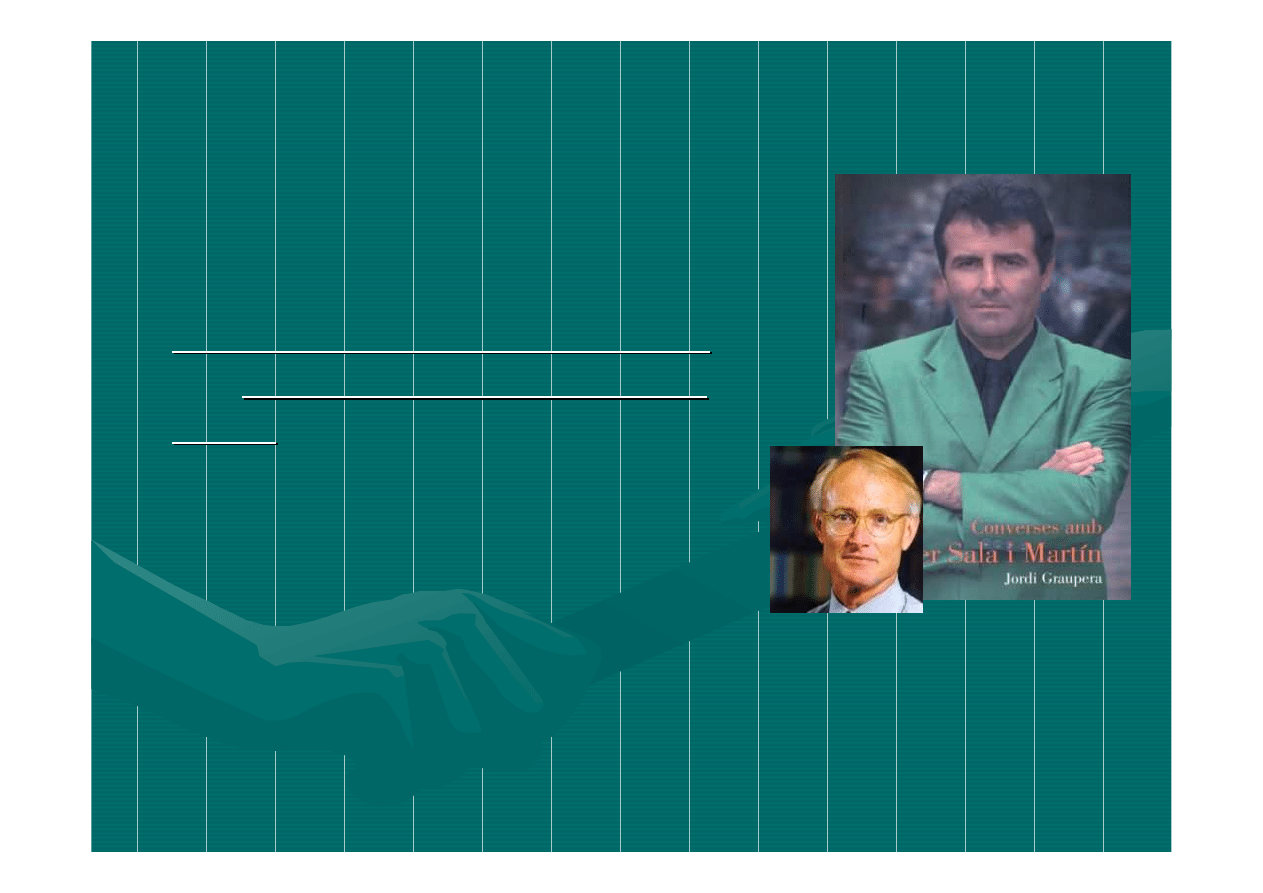
Prof.
Prof.
Xavier
Xavier
Sala
Sala
-
-
i
i
-
-
Martin
Martin
, Columbia
, Columbia
University
University
;
;
Prof.
Prof.
Michael
Michael
E. Porter,
E. Porter,
Harvard Business
Harvard Business
School
School
WEF: 12
WEF: 12
pillars
pillars
of
of
competitiveness
competitiveness
1.
1.
Institutions
Institutions
2.
2.
Infrastructure
Infrastructure
3.
3.
Macroeconomic
Macroeconomic
results
results
4.
4.
Health
Health
care
care
and
and
basic
basic
education
education
5.
5.
University
University
education
education
6.
6.
Market
Market
of
of
goods
goods
7.
7.
Labour
Labour
market
market
8.
8.
Financial
Financial
market
market
9.
9.
Technology
Technology
10.
10.
Size
Size
of
of
the
the
market
market
11.
11.
Business
Business
sophistication
sophistication
12.
12.
Innovativeness
Innovativeness
Summing up…
Summing up…
•
•
Most of methods for measuring
Most of methods for measuring
international competitiveness and
international competitiveness and
international competitive ability and
international competitive ability and
position of countries are still
position of countries are still
fragmentary
fragmentary
and not well founded theoretically
and not well founded theoretically
•
•
They are still being developed with a clear
They are still being developed with a clear
tendency to eliminate obvious drawbacks
tendency to eliminate obvious drawbacks
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Lecture POLAND Competitiv2008
Lecture POLAND Competitiv2008
Lecture 6 Performance Measurement
IR Lecture1
uml LECTURE
lecture3 complexity introduction
196 Capital structure Intro lecture 1id 18514 ppt
Lecture VIII Morphology
benzen lecture
lecture 1
Lecture10 Medieval women and private sphere
8 Intro to lg socio1 LECTURE2014
lecture 3
Lecture1 Introduction Femininity Monstrosity Supernatural
G B Folland Lectures on Partial Differential Equations
competence vs performance
4 Intro to lg morph LECTURE2014
więcej podobnych podstron