
Performance Measurement
The process of quantifying the efficiency and
effectiveness of past
Action
`
Measurement = the quantification of past action
Past action
current performance
Requires:
• Set of Metrics
• Supporting Infrastructure

The Role of Measurement
• Compliance
• Check
• Challenge
4
THE PROBLEM OF THE FROG

The Ideal Performance
Measurement System
In a perfect world, managers would be able to
design an optimum PMS that would have:
• Few measures
• Non-financials that would predict financial
performance
• The same measures throughout the whole
organisation
• Clear connections to people performance, for
compensation purposes
• Stability

Core Measurements
• Employee satisfaction
• Customer satisfaction
• Cash flow

Why Measure?
Check Position
•
Measures as a means of:
– Establishing position
– Comparing (benchmarking)
– Measuring progress
Communicate Position
•
Measures as a means of:
– Communicating performance
– Communication with the regulator
Confirm Priorities
•
Measures as a means of:
– Managing
– Management and cost control
– Focusing investment
Compel Progress
•
Measures as a means of:
– Motivation
– Communicating priorities
– Basis for reward
Adapted from Neely (1998) Measuring Business Performance
8
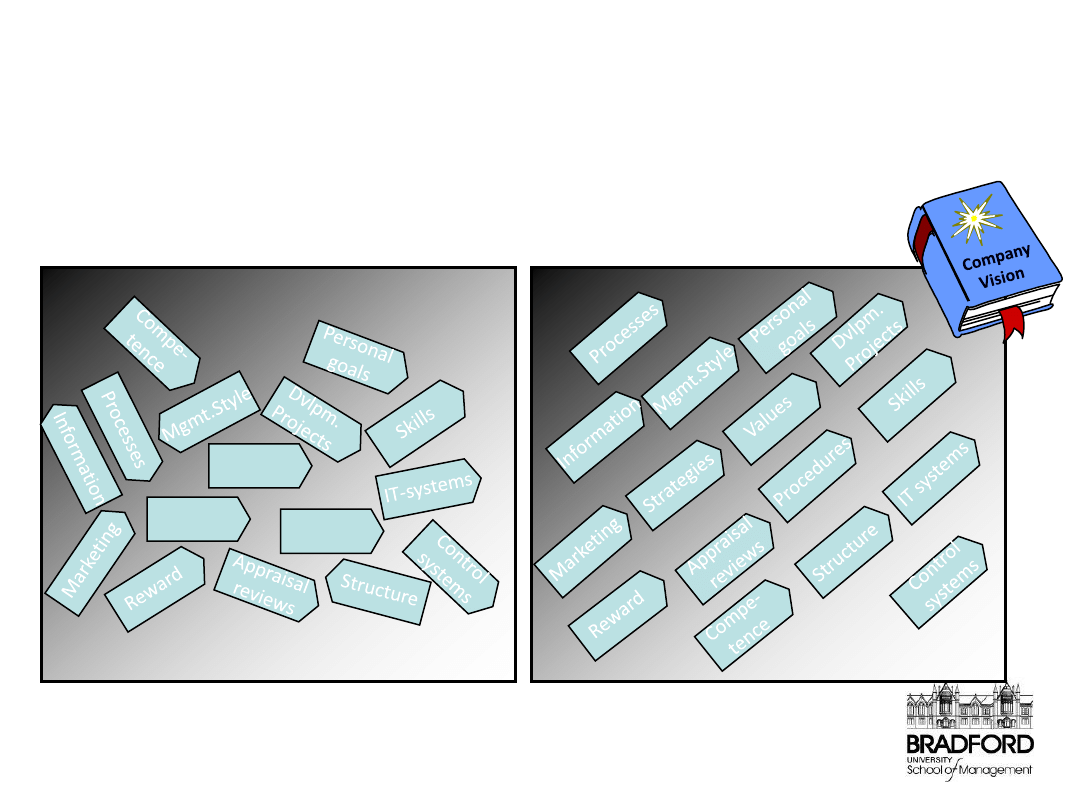
… but a lot of companies have not established this
coherence
One of the major challenges for
management today is to establish
coherence between long-term objectives
and daily operations …
Procedures
Strategies
Values
Mission
Values
Policies
Competition basis
Vision
Goals
Strategies
Success criteria
BU 1
Strategic
conditions
BU 2
Strategic
conditions
BU 3
Stratecic
conditions
BU 4
Strategic
conditions
Mission
Policies
specific to
Divisions
Competition
basis
Vision
Mission
Policies-
specific to
Divisions
Competition
basis
Vision
Mission
Policies
specific to
Divisions
Competition
basis
Vision
Mission
Policies
specific to
Divisions
Competition
basis
Vision
Objectives
Success criteria
Strategies
Projects
Objectives
Success criteria
Strategies
Projects
Success criteria
Strategies
Projects
Success criteria
Strategies
Projects
Action plan
Action plan
Action plan
Action plan
Financial plan
Financial plan
Financial plan
Financial plan
BU 5
Strategic
conditions
Mission
Policies
specific to
Divisions
Competition
basis
Vision
Objectives
Success criteria
Strategies
Projects
Action plan
Financial plan
BU 6
Strategic
conditions
Mission
Policies
specific to
Divisions
Competition
basis
Vision
Objectives
Success criteria
Strategies
Projects
Action plan
Financial plan
Top
Management
The ‘goal hierarchy’ should be consistent from top
to bottom
Often the business units work towards own goals
- not aligned with the corporate strategy
Goal
Goal
Goal
Goal
Goal
Goal
Top
Management
Objectives
Objectives
9
The reason is a common disconnect between
strategic ambition and the operational targets
which are designed to direct the daily
operations

Standards and Measures
„a “standard” is any set of agreed-upon rules for the
production of (textual or material) objects‟
Overview of the characteristics of “standards”:
• cover more than one community of practice, over time
• enable action/cooperation over distance and heterogeneity
• tend to be enforced by legal bodies
• do not reflect any natural law that the “best” will win’
• possess inertia and are therefore difficult/expensive to
change
(Bowker and Star,1999:14)
Principles Of A Performance
Measurement System (PMS)
11
CONTROL OF
EXECUTION
REPORT
FORECAST
PLAN

PMS Development
• Define an appropriate hierarchical organisation structure.
• Identify the key variables that determine performance.
• Establish Key Performance Indicators.
• Set and agree objectives, plans and targets.
• Obtain timely and accurate information defining achievement of
objectives, plans and targets.
• Implement focused Action Review meetings
• Identify problems and constraints that prevent achievement and take
appropriate remedial action.

Control of
Execution
Report
Review
at an appropriate
interval
Use to indicate
achievement against
targets
Merchandise
success
Feedback performance
Surface problems
Initiate action to rectify,
recover, prevent
Track, adjust, refine
Performance data
only
Indicate trends /
patterns
Achievement
improvement
Management Control Process
13
Forecast
Plan
Expected
outcomes
Trends
Agree & publish
Detailing of
forecast into
shorter time-
frames
Agree & publish
Vision
Objectives
Balance demand &
output
Regulate activities
Eliminate
bottlenecks
Smooth work flow
Track, adjust,
refine
Establish
sequence &
priorities
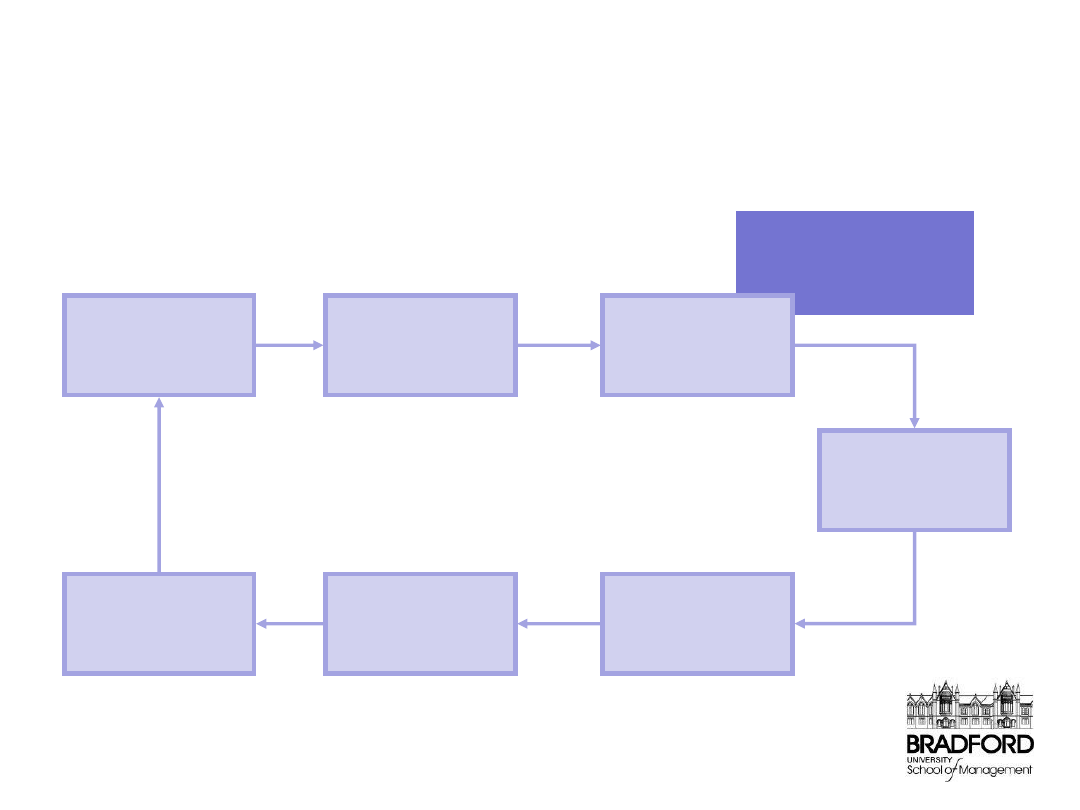
Management Report
Control/Review Stage - Feedback Loop
Implement
Corrective
Action
Planned
Performance
Actual
Performance
Comparison
of Actual vs
Plan
Identification
of Variance
Cause
Analysis
Determine
Corrective
Action
Action Review Meeting Process

Essential components of robust management
reporting system:
• Clear organisational structure.
• Structured information system.
• Disciplined review process.
Management Reporting
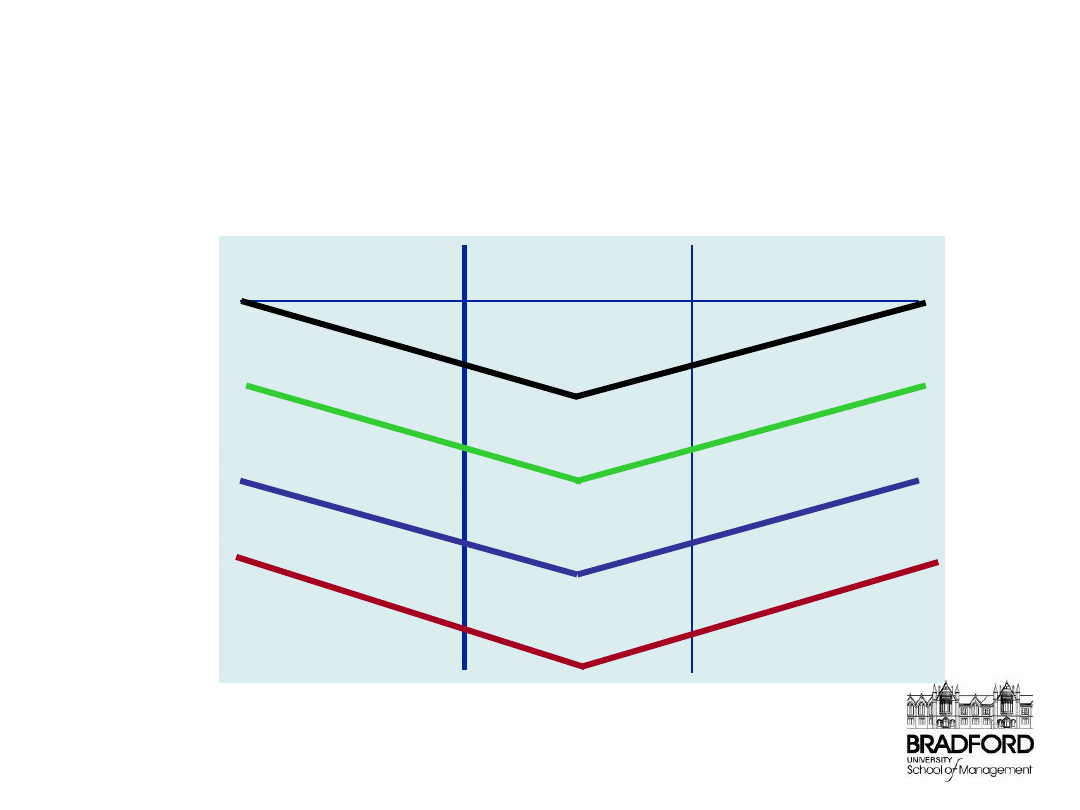
Typical hierarchy of control / review frequency
PLAN
REVIEW
REPORT
Board of Directors
Departmental
Manager
Supervisor
Weekly
Monthly
Annually/
Quarterly
Hourly
Daily
Management Reporting
Management
Team
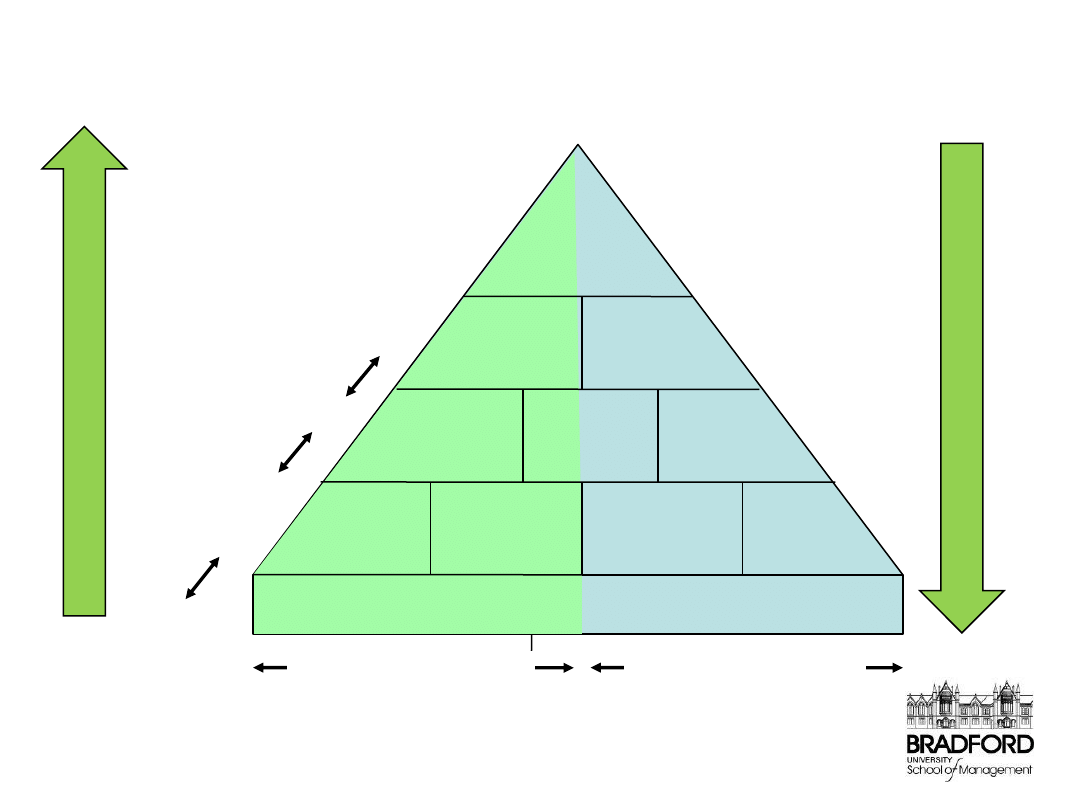
The Performance Pyramid
The Strategic Measurement and Reporting Technique (SMART) pyramid; Adopted from Lynch and Cross (1991)
Corporate
Vision
Market
Financial
Productivity
Flexibility
Customer
Satisfaction
Waste
Cycle Time
Delivery
Quality
Performance Management Systems
Internal Effectiveness
External Effectiveness
Business units
Departments,
groups and
work teams
Core business processes
Individuals
Mea
sure
s
Obje
ctives
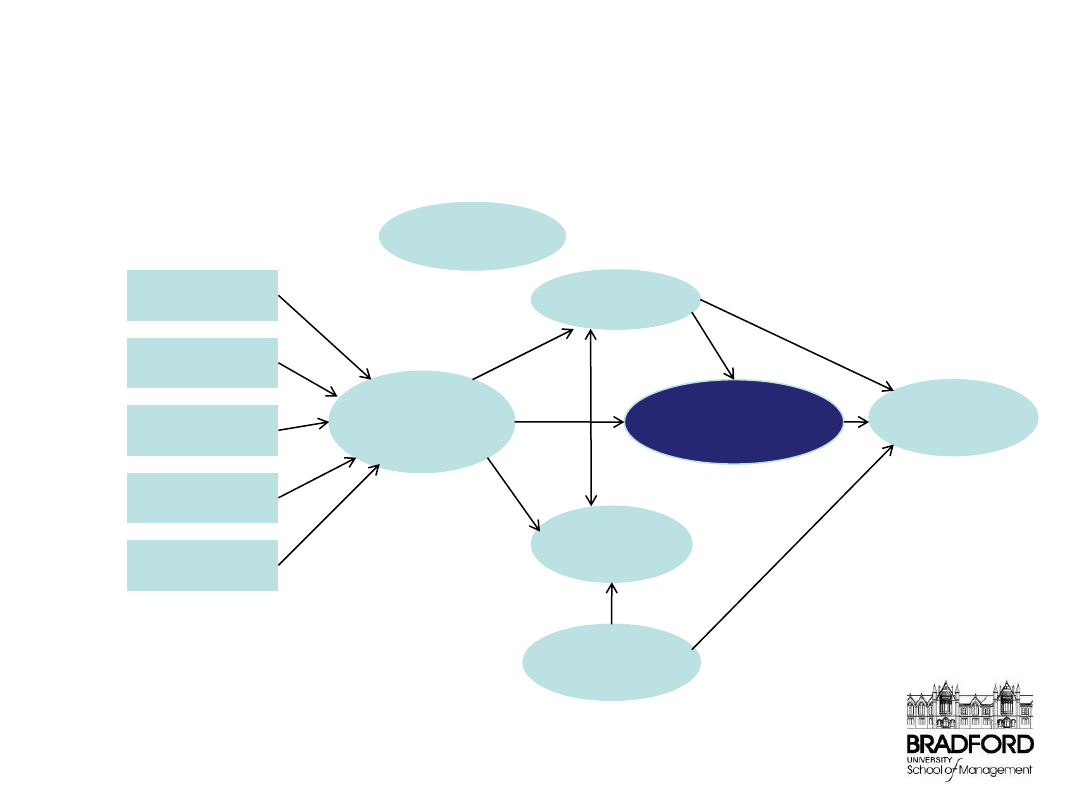
The Drivers of Customer
Satisfaction
Adapted from BT Mobile
– a Customer Services Project
After-Sales
Sales Team
Shop
Reseller
Provision
Quality of
Service
Loyalty
Price
Perception
Satisfaction
Value for
Money
Image
Reliability
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
pcnasr performance measures
Lecture 9 Performance Prism
Lecture 1 Business Performance Management
Lecture 12 Where Next for Performance Management
Lecture 2 Measuring competitiveness
Lecture 10 Frameworks for Quality Performance Management
Guidelines For Measuring Audio Power Amplifier Performance (Texas Instruments)
IR Lecture1
uml LECTURE
lecture3 complexity introduction
PERFORMANCE LEVEL, PL
196 Capital structure Intro lecture 1id 18514 ppt
Lecture VIII Morphology
benzen lecture
lecture 1
Lecture10 Medieval women and private sphere
8 Intro to lg socio1 LECTURE2014
Herbs for Sports Performance, Energy and Recovery Guide to Optimal Sports Nutrition
więcej podobnych podstron
