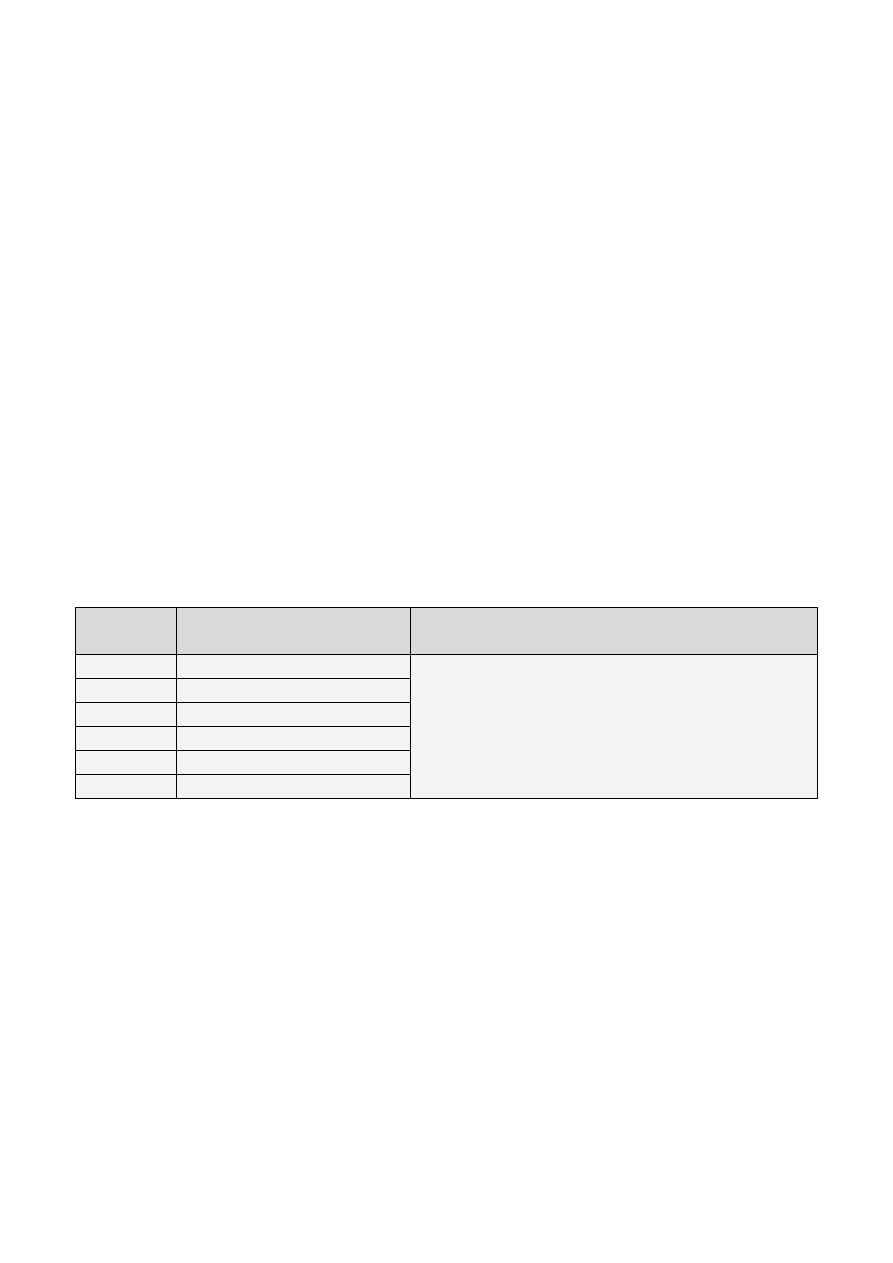
Past Continuous
Czas przeszły ciągły
I. Form
Tworzenie czasu
Positive sentences
Forma twierdząca
Yesterday at 5 o’clock I was working on my computer.
When I opened the door, the secretary was arranging a meeting on the phone, clerks were working at their
desks and the managers were discussing the matters of life and death for the company.
The positive form of the present continuous tense is formed with the past tense of the verb to be and the
present participle.
Formę twierdzącą czasu teraźniejszego ciągłego tworzymy poprzez dodanie imiesłowu czasu teraźniejszego
do czasownika to be w czasie przeszłym.
Subject
Podmiot
Verb to be (past)
Czasownik to be (czas przeszły)
Present Participle
Imiesłów czasu teraźniejszego
I
was
working
arranging
talking
playing
studying
discussing
you
were
he, she, it
was
we
were
you
were
they
were
Remember
Zapamiętaj
to be (was,were) + -ing
Spelling
Pisownia
The spelling of the present participle is same as for the present continuous tense.
Pisownia imiesłowu czasu teraźniejszego jest identyczna jak w czasie teraźniejszym ciągłym.
Negative
Forma przecząca
You were not playing tennis then.
She wasn’t talking.
You were not listening to me.
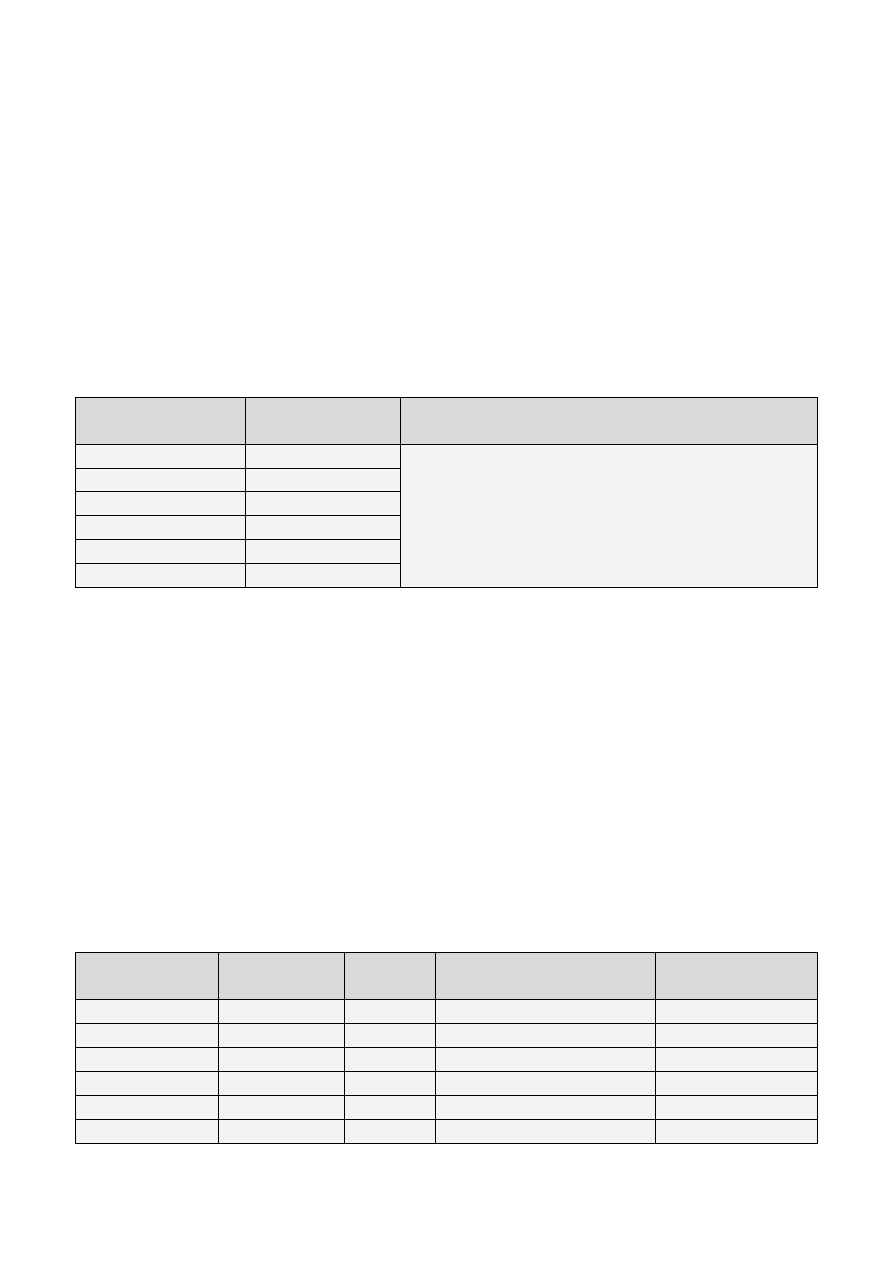
The negative form of the past continuous tense is formed with the past tense of the verb to be followed by
not and the present participle.
Formę twierdzącą czasu przeszłego ciągłego tworzymy poprzez dodanie imiesłowu czasu teraźniejszego do
czasownika to be w czasie przeszłym, po którym występuje not.
Full form
Forma pełna
Contracted form
Forma ściągnięta
Present Participle
Imiesłów czasu teraźniejszego
I was not
I wasn’t
playing
talking
listening
working
studying
swimming
you were not
you weren’t
he, she, it was not
he, she, it wasn’t
we were not
we weren’t
you were not
you weren’t
they were not
they weren’t
Remember
Zapamiętaj
to be (was/were) + not + -ing
Questions
Forma pytająca
Were you watching TV then?
What dress was she wearing that day?
To make questions, we use the same auxiliary verb and change the word order in the sentence.
Do tworzenia pytao używamy tego samego operatora i zmieniamy kolejnośd wyrazów w zdaniu.
Question word
Zaimek pytający
Auxiliary Verb
Operator
Subject
Podmiot
Present Participle
Imiesłów czasu teraźniejszego
Were
you
watching
TV then?
Were
you
feeling
OK?
Was
she
swimming
then?
What
were
you
doing
at 5 o’clock?
What dress
was
she
wearing
that day?
Where
were
you
going
that evening?
Remember
Zapamiętaj
to be (was/were) + subject + -ing
to be (was/were) + podmiot + -ing
or
lub
question word + to be (was/were) + subject + -ing
zaimek pytający + to be (was/were) + podmiot + -ing
Short answers
Krótka odpowiedź
“Was Jamie taking a shower then?” “Yes, he was.”
Yes, I was
No, I was not.
Yes, he, she, it was.
No, he wasn’t, she’s wasn’t, it’s wasn’t.
Yes, we, you, they were.
No, we weren’t, you weren’t, they weren’t.
II. Use
Użycie czasu
The present continuous tense is used mainly to talk about events which continued for some time, but their
time limits are unknown or are not important.
Czas przeszły ciągły używany jest głównie do mówienia o czynnościach, które trwały przez jakiś czas, ale ich
ramy czasowe są nieznane lub nieistotne.
It was snowing then.
It was getting darker.
He was taking a shower.
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Czas Past Continuous (przeszły ciągły)
Franz Stanzel - Sytuacja narracyjna i epicki czas przeszły, Kulturoznawstwo, literaturoznawstwo
Czas przeszły niedokonany
CZAS PRZESZŁY IMPERFETTO, 9. Sussidi didattici, GRAMMATICA
Czas przeszly
PERFEKT czas przeszL,y zL,oLzo Nieznany
CZAS PRZESZŁY PASSATO PROSSIMO, 9. Sussidi didattici, GRAMMATICA
Czas przeszły
Czas przeszły imperfetto (2), język włoski
Hiszpański- Czas przeszły - Pretérito czasowniki, języki obce, hiszpański, Język hiszpański
czas przeszly dokonany das Perfekt, ✔ GRAMATYKA W OPISIE OD A DO Z
Czas przeszły passato prossimo(1), język włoski
czas przeszły dla klasy czwartej
Czas przeszły dokonany
Borucki - czas przeszły czasownika, rusycystyka
Franz Stanzel - Sytuacja narracyjna i epicki czas przeszły, Kulturoznawstwo UŚ, Semestr I
czas przeszły, Nauka polskiego FOR FOREIGNERS
CZAS PRZESZŁY ZŁOŻONY - odmiana być
Czas przeszły imperfetto, język włoski
więcej podobnych podstron