
PROBLEMY
ZDROWIA W
SKALI
MIĘDZYNAROD
OWEJ
wykład 4
2014

EUROPEJSKIE CENTRUM DS.
ZAPOBIEGANIA I KONTROLI CHORÓB
Europejskie Centrum ds.
Zapobiegania i Kontroli Chorób
(ECDC) zostało utworzone w 2005 r.
Jest to agencja Unii Europejskiej,
której celem jest wzmacnianie
ochrony przed chorobami zakaźnymi
w Europie.
Siedziba Centrum mieści się w
Sztokholmie (Szwecja).

POWOŁANIE ECDC
Centrum powołano na podstawie
rozporządzenia nr 851/2004
Parlamentu Europejskiego i Rady
z dnia 21 kwietnia 2004 r.
ECDC rozpoczęło działalność 20
maja 2005 r.

MISJA ECDC
Misją ECDC jest identyfikacja,
ocena i powiadamianie o bieżących
i pojawiających się zagrożeniach
dla zdrowia ludzkiego ze strony
chorób zakaźnych, a także
wspieranie i pomoc w koordynacji
gotowości oraz reagowania na
takie zagrożenia w krajach Unii
Europejskiej.

CEL ECDC
Zwiększenie ochrony przed chorobami
zakaźnymi,
np. grypą, SARS oraz HIV/AIDS.
Wzmocnienie i rozwój nadzoru
epidemiologicznego oraz systemów
wczesnego ostrzegania.

ZADANIA
zwiększenie zdolności Wspólnoty oraz
państw członkowskich w zakresie ochrony
zdrowia ludzkiego poprzez zapobieganie
chorobom i ich kontrolę;
działanie z własnej inicjatywy w przypadku
pojawienia się choroby zakaźnej nieznanego
pochodzenia zagrażającej Wspólnocie;
zapewnienie uzupełniających się i spójnych
działań w dziedzinie zdrowia publicznego
przy uwzględnieniu zadań i obowiązków
państw członkowskich, instytucji unijnych
oraz właściwych organizacji
międzynarodowych.

MISJA ECDC
Partnerstwo z narodowymi
instytucjami zajmującymi się
ochroną zdrowia
Wzmocnienie i rozwój
europejskiego systemu
nadzoru i wczesnego
ostrzegania
Rola ekspertów
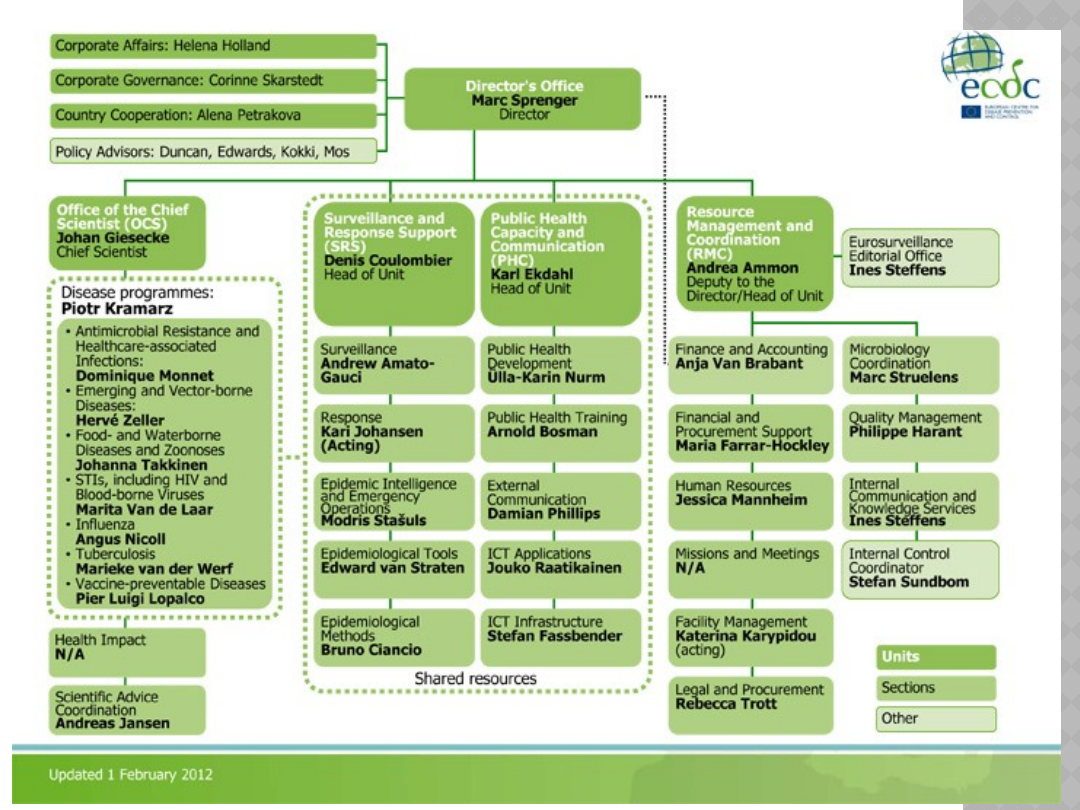

STRUKTURA
ORGANIZACYJNA ECDC
Office of the Chief Scientist
(OCS)
Surveillance and Response
Support (SRS)
Public Health Capacity and
Communication (PHC)
Resource Management and
Coordination (RMC)

MISJA ECDC
(a) search for, collect, collate, evaluate and disseminate
relevant scientific and technical data;
(b) provide scientific opinions and scientific and
technical assistance including training;
(c) provide timely information to the Commission, the
Member States, Community agencies and
international organisations active within the field of
public health; coordinate the European networking
of bodies operating in the fields within the Centres
mission, including networks arising from public
health activities supported by the Commission and
operating the dedicated surveillance networks;
(e) exchange information, expertise and best practices,
and facilitate the development and implementation
of joint actions.

OFFICE OF THE CHIEF
SCIENTIST (OCS)
Disease Programmes: .
Health Impact:
Scientific Advice Coordination:
Additionally, responsibilities and
resources for developing and
maintaining an in-house programme to
ascertain a high level of public health
knowledge among the staff are based in
this Office.

OFFICE OF THE CHIEF SCIENTIST
(OCS) DISEASE PROGRAMMES:
1.
antibiotic resistance and healthcare-
associated infections;
2.
emerging and vector borne diseases;
3.
food- and waterborne diseases;
4.
HIV, sexually transmitted infections
and hepatitis;
5.
influenza;
6.
tuberculosis;
7.
vaccine-preventable diseases.

OFFICE OF THE CHIEF
SCIENTIST (OCS)
Health Impact: Developing over-arching
projects, such as environmental determinants –
including climate change – of infections, as well
as assessing the burden of infectious disease in
the EU.
Scientific Advice Coordination: Managing the
Centre’s process of handling requests for
scientific advice, and developing evidence-based
methods for public health.
Additionally, responsibilities and resources for
developing and maintaining an in-house
programme to ascertain a
high level of public
health knowledge among the staff
are based in
this Office.

SURVEILLANCE AND
RESPONSE SUPPORT (SRS)
Surveillance
Response:
Epidemic Intelligence and
Emergency Operations:
Epidemiological Tools:
Epidemiological Methods:

SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE
SUPPORT (SRS) SURVEILLANCE:
to contribute to reducing the incidence and
prevalence of communicable disease in Europe
by
providing relevant public health data,
clear analysis,
information and reports
to decision makers, professionals and healthcare
workers in Member States, other public health
agencies and key stakeholders
to ensure more informed decision making for
actions that will result in the timely prevention
and control of communicable diseases in
Europe.

SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE
SUPPORT (SRS) RESPONSE:
Coordinating the response support
functions in ECDC in order to provide
timely support to Member States and
the European Commission regarding
requests for
risk assessments,
threat investigations,
and provision of experts in the field when
requested.

SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE
SUPPORT (SRS) EPIDEMIC
INTELLIGENCE AND EMERGENCY
OPERATIONS:
Ensuring
early detection of emerging threats to the EU,
their analysis,
and the feed back to Member States and
stakeholders
through daily, weekly and annual threat reports.
Maintaining
the Emergency Operating Centre (including ICT
and communication capacity),
plans (public health event plan)
and procedures (24/7 duties…)
to ensure optimal support to management of
public health emergencies.

SURVEILLANCE AND
RESPONSE SUPPORT (SRS)
Epidemiological Tools: Developing,
maintaining and supporting ECDC data
bases and communication platforms
related to its mandate, e.g. TESSy,
EWRS, EPIS platforms.
Epidemiological Methods: Developing
and harmonising methods used for
surveillance and response to
communicable disease threats, in terms
of surveillance standards and
developments, biostatistics and spatial
analysis.

SURVEILLANCE AND
RESPONSE SUPPORT (SRS)
The European Surveillance System
(TESSy)
TESSy, EWRS, EPIS platforms.

PUBLIC HEALTH CAPACITY
AND COMMUNICATION (PHC)
Public Health Development: Providing expertise and support to Member
States, stakeholders and other ECDC programmes in the areas of
communication knowledge, behaviour change, programme evaluation, social
determinants, health economy and preparedness in order to prevent and
control communicable diseases. The work is based on a solid understanding of
the public health structures in Europe.
Public Health Training: Strengthening public health capacities in Europe
through coordinating the EPIET and EUPHEM programmes, providing short
courses and programmes for training the trainers and continuing education of
experts. Strengthening training networks and progressively implementing
innovative methods and tools for teaching.
External Communication: Efficiently communicating ECDC scientific and
technical knowledge to promote public health. Raising awareness of the impact
of communicable diseases and the importance of their prevention and control.
Application Support and Development: Developing and supporting key
ECDC information systems. Fostering Europe-wide cooperation in the area of
public health informatics.
ICT Infrastructure: Providing ICT support services to benefit all ECDC
activities. Networking on ICT issues with other EU agencies and the European
Institutions.
All activities are carried out in close cooperation with other units of ECDC as
well as with external partners across Europe and globally.

RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
AND COORDINATION (RMC)
Resource Management
Human Resources Section: Promoting a supportive work environment that attracts,
develops and motivates a multicultural and highly professional work force by providing high
quality services based on competent advice and communication with the ECDC’s staff and
management.
Finance and Accounting Section: Ensuring that the financial resources of the Centre are
managed efficiently and reported in a clear and comprehensive manner. Execute all payments
of the Centre. Provide financial verification of commitments. Provide the annual accounts of
the Centre which present a true and fair view of the financial position of the Centre. Provide
budgetary reporting on the implementation of the budget and its transfers.
Financial and Procurement Support Section: Providing support and advice to authorising
officers to allow them taking informed decisions for all legal or budgetary commitments.
Monitor and follow up all procurement procedures, commitments and contracts ensuring
efficiency and effectiveness of the operation as well as the legality and regularity of the
operation.
Mission and Meetings Section: Organising travel and hotel arrangements and providing
budget verification, monitoring and processing of reimbursement claims for staff, interviewees
and experts invited to ECDC with a high level of service attitude and ensuring an economically
prudent use of ECDC’s travel budget.
Facility Management Section: Developing and maintain the premises of the Centre to meet
the requirements of a growing organisation, provide logistics services for the operational
activities, provide logistics services to staff and maintain physical inventory.
Legal and Procurement Section: Providing legal advice and assistance to all Units and
ensuring compliance with data protection requirements. Coordinating all procurement
procedures and running the Committee on Procurements, Contracts and Grants to ensure
compliance with relevant rules and regulations

RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
AND COORDINATION (RMC)
Coordination
Microbiology Coordination: Striving to strengthen the capacity and capability of
the EU public health microbiology system to provide timely and reliable
information for infectious disease prevention and control at Member State and EU
levels.
Quality Management: Implementing a quality management system
encompassing all areas of work in the Centre, and ensuring coordination of the
Work Programme by providing the technical tools to all Units to plan and monitor
the implementation of their activities more efficiently.
Internal Communication and Knowledge Services: Aiming at a coherent and
transparent stream of information and quick access to relevant information for all
staff. Facilitating the free flow of knowledge and information across the Centre to
enable ECDC to act as one team and supporting through networking a broad
sharing of knowledge services.
Internal Control Coordinator: Providing advice, coordination and expertise in
Internal Control activities, including risk management, the Internal Control
Standards, the Internal Procedures and the Director’s Declaration of Assurance.
Coordinating relations with the Audit Committee and the Internal Audit Service,
including coordination of the follow-up on all audit recommendations.
Eurosurveillance Editorial Office: Responsible for the independent scientific
journal on surveillance, prevention and control of infectious diseases published by
ECDC. Providing a platform for exchange of scientific disease information among
experts in Europe and worldwide, free of charge for readers and authors.

COMPETENT BODIES
1.
Austria
Ministry of Health: Directorate General Public Health and Medical Affairs
2.
Belgium
Scientific Institute of Public Health
3.
Bulgaria
National Center of Infectious and Parasitic Diseases
4.
Cyprus
Ministry of Health: Directorate of Medical and Public Health Services, Surveillance
Unit
5.
Czech Republic
National Institute of Public Health
6.
Denmark
National Board of Health
7.
Estonia
Health Board
8.
Finland
National Institute for Health and Welfare
9.
France
Institute for Public Health Surveillance
10.
Germany
Robert Koch Institute
11.
Greece
Hellenic Centre for Disease Control and Prevention
12.
Hungary
National Center for Epidemiology
13.
Iceland
Centre of Health Security and Communicable Disease Control: Directorate of Health
14.
Ireland
Health Protection Surveillance Centre
15.
Italy
Ministry of Health: Communicable Diseases Unit
16.
Latvia
State Agency "Infectology Center of Latvia"
17.
Liechtenstein
Liechtensteinische Landesverwaltung: Office of Public Health
18.
Lithuania
Ministry of Health: Public Health Department
19.
Luxembourg
Health Directorate/Direction de la Santé
20.
Malta
Ministry for Health, the Elderly and Community Care: Superintendence of Public Health
21.
Netherlands
National Institute for Public Health and the Environment: Centre for Infectious
Disease Control
22.
Norway
Norwegian Institute of Public Health: Division of Infectious Disease Control
23.
Poland
Chief Sanitary Inspectorate
24.
Portugal
Ministry of Health: Directorate General of Health
25.
Romania
National Institute of Public Health: National Centre for Communicable Diseases and
Surveillance and Control
26.
Slovakia
Public Health Authority of the Slovak Republic
27.
Slovenia
National Institute of Public Health: Centre of Communicable Diseases
28.
Spain
Ministry of Health, Social Services and Equality: General Directorate of Public Health,
Quality and Innovation
29.
Sweden
Swedish Institute for Communicable Disease Control
30.
United Kingdom
Health Protection Agency: National Infectious Diseases Surveillance Centre

DISEASE PROGRAMMES:
Antimicrobial Resistance and
Healthcare-associated Infections
Emerging and Vector-borne Diseases
Food- and Waterborne Diseases and
Zoonoses
STI, including HIV and Blood-borne
Viruses
Influenza
Tuberculosis
Vaccine-preventable Diseases

ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE AND
HEALTHCARE-ASSOCIATED
INFECTIONS
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR), i.e. the ability of
microorganisms to become resistant to one or several
antimicrobial agents used for therapy or prophylaxis;
Healthcare-Associated Infections (HAI), i.e. all
infections associated with patient care, in particular
hospitals and long-term care facilities.
The ARHAI programme focuses on 4 areas of public
health:
surveillance,
response and scientific advice,
training
and communication
to address the threat of antimicrobial resistance and
healthcare-associated infections.

EUROSURVEILLANCE
ARTICLES
The European gonococcal antimicrobial surveillance
programme, 2009 20 October 2011
Trends in yearly prevalence of third-generation
cephalosporin and fluoroquinolone resistant
Enterobacteriaceae infections and antimicrobial use in
Spanish hospitals, Spain, 1999 to 2010, 06 October 2011
Imported extensively drug-resistant Mycobacterium
tuberculosis Beijing genotype, Marseilles, France, 2011
21 April 2011
Rapid increase of carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella
pneumoniae strains in a large Italian hospital:
surveillance period 1 March - 30 September 2010 24
February 2011
First identified case of VIM-producing carbapenem-
resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in the Republic of Ireland
associated with fatal outcome 16 December 2010
Antimicrobial resistance 2010: global attention on
carbapenemase-producing bacteria 18 November 2010

EUROSURVEILLANCE
ARTICLES
Possible importation and subsequent cross-
transmission of OXA-48-producing Klebsiella
pneumoniae, France, 2010 18 November 2010
New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase 1-producing
Enterobacteriaceae: emergence and response in
Europe 18 November 2010
Prevalence of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus
aureus amongst professional meat handlers in the
Netherlands, March-July 2008, 18 November 2010
Carbapenem-non-susceptible Enterobacteriaceae in
Europe: conclusions from a meeting of national
experts, 18 November 2010
Extended measures for controlling an outbreak of VIM-
1 producing imipenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae
in a liver transplant centre in France, 2003-2004, 18
November 2010

EUROSURVEILLANCE
ARTICLES
Appropriateness of antimicrobial therapy: a
multicentre prevalence survey in the Netherlands,
2008-2009, 18 November 2010
Eurobarometer on antimicrobial resistance
highlights areas for action, 15 April 2010
Dispensing of antibiotics without prescription in
Greece, 2008: another link in the antibiotic
resistance chain, 18 February 2010
Antibiotic resistance in Europe: the challenges
ahead, 12 November 2009
Document Outline
- Slide 1
- Europejskie Centrum ds. Zapobiegania i Kontroli Chorób
- Powołanie ECDC
- MIsja ECDC
- Cel ECDC
- Zadania
- MIsja ECDC
- Slide 8
- Struktura organizacyjna ECDC
- MIsja ECDC
- Office of the Chief Scientist (OCS)
- Office of the Chief Scientist (OCS) Disease Programmes:
- Office of the Chief Scientist (OCS)
- Surveillance and Response Support (SRS)
- Surveillance and Response Support (SRS) Surveillance:
- Surveillance and Response Support (SRS) Response:
- Slide 17
- Surveillance and Response Support (SRS)
- Surveillance and Response Support (SRS)
- Public Health Capacity and Communication (PHC)
- Resource Management and Coordination (RMC)
- Resource Management and Coordination (RMC)
- Competent Bodies
- Disease programmes:
- Antimicrobial Resistance and Healthcare-associated Infections
- Eurosurveillance articles
- Eurosurveillance articles
- Eurosurveillance articles
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Problemy zdrowia w skali międzynarodowej wykład 2 2014
Problemy zdrowia w skali międzynarodowej wykład 3 2014
Problemy zdrowia w skali międzynarodowej wykład 2 2014
Problemy zdrowia w skali międzynarodowej wykład 1 2015
Trzeciak problemy zdrowia w skali międzynar
Trzeciak problemy zdrowia w skali międzynar (1)
GIEŁDA Poblemy zdrowia w skali międzynarodowej
MIĘDZYNARODOWE PROBLEMY ZDROWIA 4
MIĘDZYNARODOWE PROBLEMY ZDROWIA 1
Unia Europejska jako aktor stosunkow miedzynarodowych wyklad ZIEBY
Komercyjne usługi seksualnego jako problem zdrowia publicznego
Palestynski problem tekst, Politologia, Międzynarodowe Stosunki Polityczne
Wprowadzenie w problematykę zdrowia.popr, KOSMETOLOGIA, Higiena i promocja zdrowia
Marketing międzynarodowy wykład 1
29 splot szyjny i nerwy międzyżebrowe, Wykłady anatomia
Finanse międzynarodowe WYKŁAD 8
FINANSE MIĘDZYNARODOWE WYKŁAD 5
finanse miedzynarodowe wyklady
więcej podobnych podstron