
Background
• From Taylor to Skinner, through the
Quality gurus, an increasing requirement
to measure throughout business
• Led to ― the unanticipated consequences
of measurement” (Ridgway, 1956)
• Balanced set of measures first mooted by
Drucker in 1954 as a potential solution
solution to the issues raised by these
themes.

Balanced Measures
“ market standing, innovation, productivity,
physical and financial resources,
profitability, manager performacne and
development, worker performance and
attitude, and public responsibility”
…..are all appropriate performance criteria
Drucker(1954:??)

Balanced Business Scorecard
is both a process and a tool
– Thinking process
to define what constitutes
a thriving business, and what matters most to
your business
– Communications tool
to tell people what
they need to do to achieve success
– Management tool
to trace performance
problems to their cause

The Balanced Scorecard
What it does:
• Measures the achievement of the
business strategy
• Communicates strategic direction
• Establishes key performance measures
and performance targets at the
organisational level
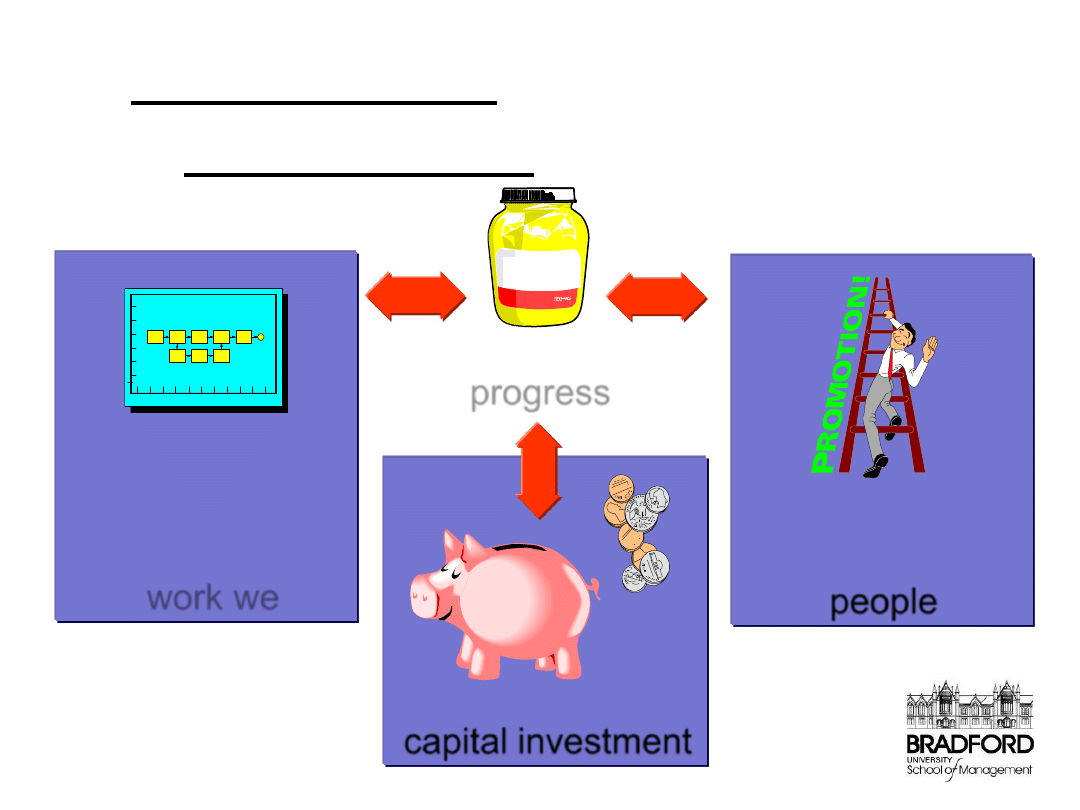
Measurement links the 3 areas
of Management in any business
How we manage
the work we do
How we manage
people
How we manage
capital investment
GLUE
How we measure
progress
Using the scorecard to drive a
performance culture
Team Target Setting
Linkage to Change Programmes
Team Accountability & Rewards
Bottom Up Goal Setting
Corporate Linkage: Organisation Design
The Vision
Learning
Feedback
Systems
1. The Creation Phase
Develop the scorecard.
Clarify
the vision and gain
executive
consensus
2. The Deployment Phase
Communicate the vision
to all levels of the
organisation and create
team scorecards
4. The Ongoing Improvement Phase
Integrate the scorecard into the
management process
• monthly management review
• strategic planning update
3. The Commitment Phase
Deploy the scorecard down to
individuals and embed them in
the reward system
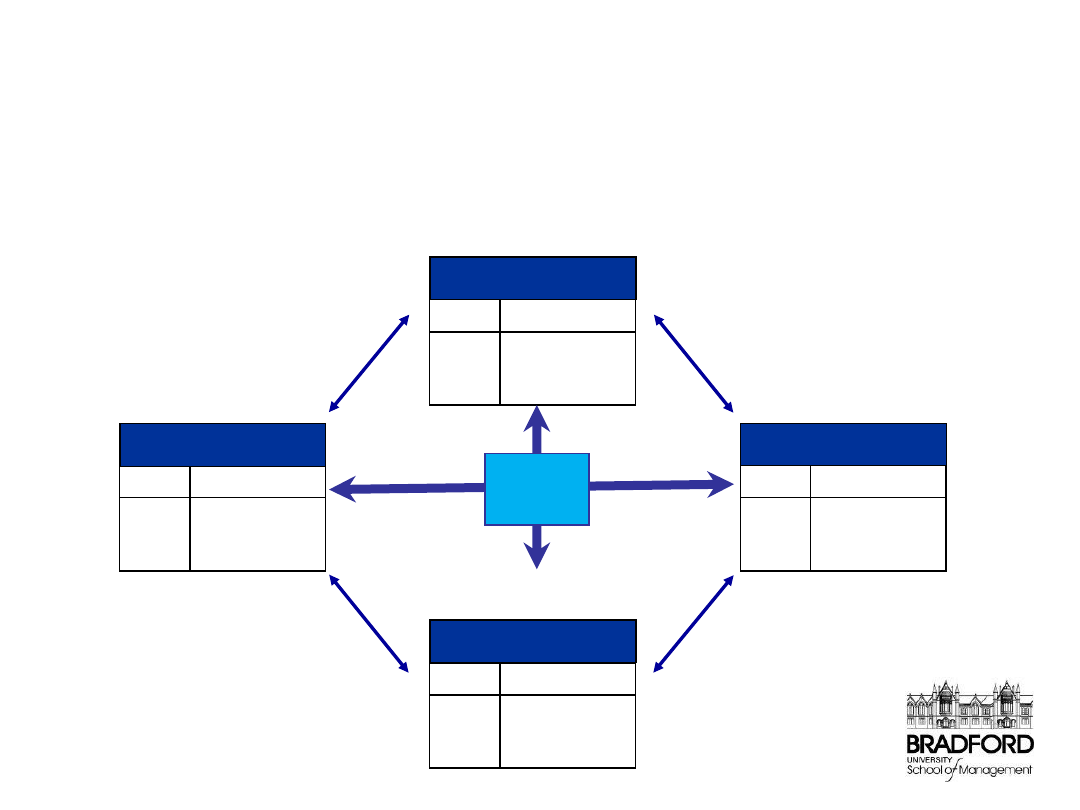
The Four Perspectives
How do we look to
shareholders?
What must we
excel at?
Can we continue to
improve and add value?
How do customers
see us?
GOALS MEASURES
Customer
Perspective
Financial
Perspective
GOALS MEASURES
Innovation & Learning
Perspective
GOALS MEASURES
Internal Business
Perspective
GOALS MEASURES
Vision
and
Strategy

The components
• Goals/objectives – needs to articulate
them into observable and measurable
parts
• Metrics – actionable and tangible, support
the tracking of achieving the objects
• Targets – performance level expectations
set against the strategic plan

A Balanced Scorecard……..
• Provides managers with the instrumentation they need to
navigate to future competitive success
• Provides executives with a comprehensive framework
that translates a company’s vision and strategy into a
coherent set of performance measures
• The whole organisation understands how they are
contributing to the achievement of the vision of an
organisation
• Enables businesses to look and move forward rather
than backward
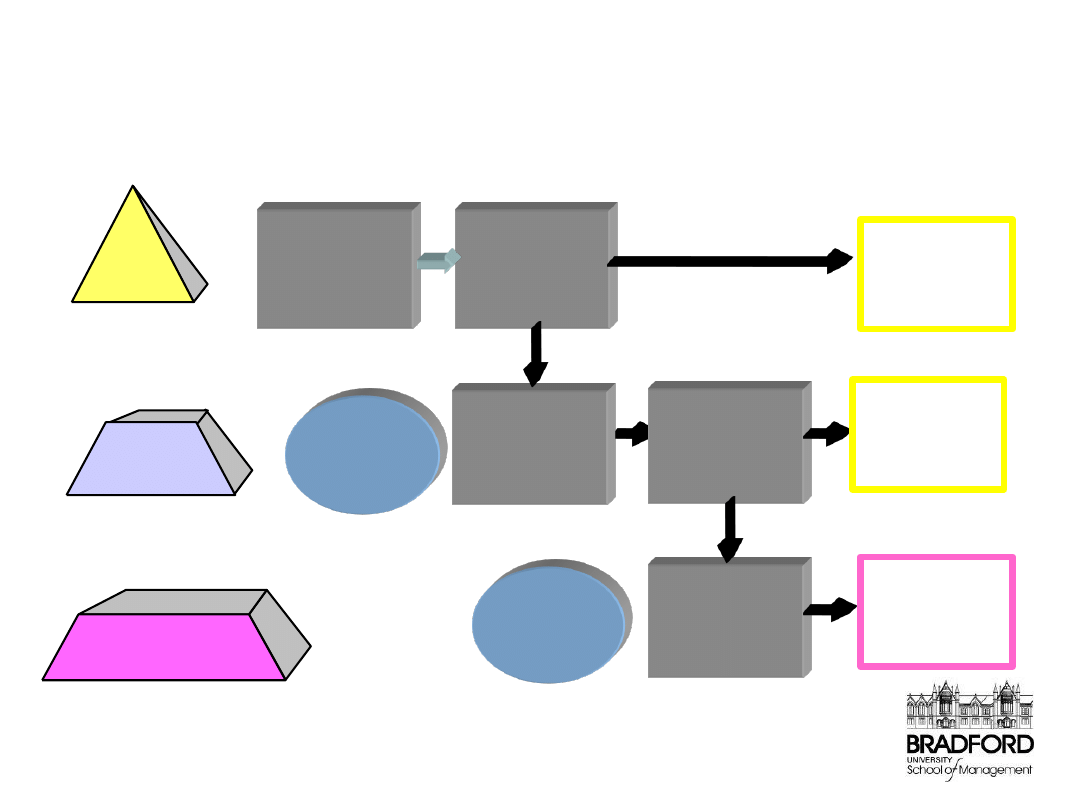
The Scorecard Architecture
Organization
Group/ Department
Individual
Select
group
impactable
CSFs
Identify
organisational
objectives to
reach strategy
Identify
organisational
strategy
Group/
department
measures and
metrics
Group/
department
objectives
Individual
goals
Select
individual
impactable
CSFs
Organisation
level
scorecard
Group
/department
level
scorecard
Individual
measures &
metrics
scorecard
Common questions #1:
How many measures?
•
Longevity:
– businesses
change
;
some change very fast
– focus on individual
measures also
changes
– it takes
time to
implement
performance
measurement
frameworks and tools
– better to have over-
catered than under-
catered...
– … so long as you
support this with
appropriate
technology
•
Technology:
– most
Executive
Information Systems
allow you to set
thresholds
– good management
focuses on those
measures that have
dropped below a
certain threshold
– so at any one time the
technology can
filter
out only a small
number of
critical
measures, from a pool
of
useful
measures
Accountabilities:
•
Balanced Business Score
Cards assume a
cascade
of information
•
at any one time, any one
individual, should have
only a small number of
measures to consider
•
but these measures
combine and aggregate
•
… for example

Common questions #2:
Why is it called ―balanced‖?
– Balance of measures
• at least 4 areas of measurement
• not all financial
– Balance of types of measure
• leading and lagging measures
• helps to forecast and follow through
• not just ―oh dear, haven’t we done badly last month!‖
– Balance of how measures are used
• cascade encourages teamwork
• ―detective search‖ for the causes of underperformance
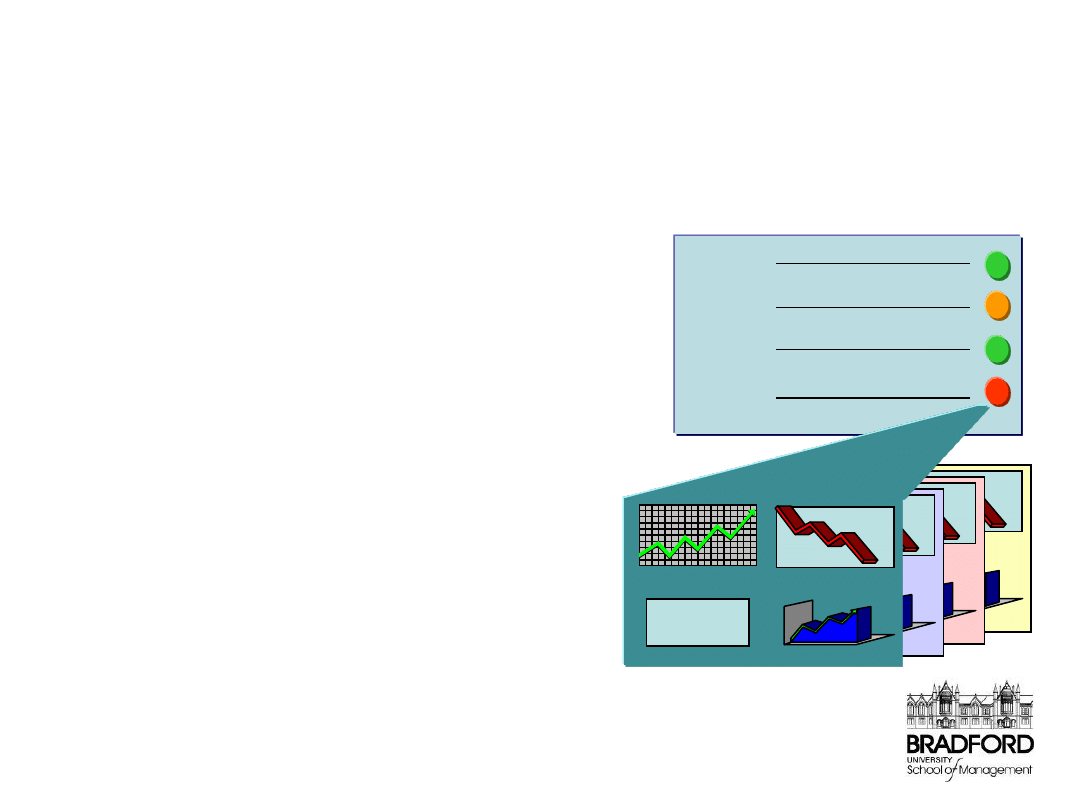
Common questions #3:
So how is it used?
– Performance Dashboard
and Traffic Light Reports
• flag measures that
have gone critical/are
going critical
• focus attention on
where it matters most
• communicate why
certain action is
required
• provide feedback on
the results of past
action
– Actions are set as a result
of regular review of the
dashboard
Measure 1
Measure 2
Measure 3
Measure 4
Measure 1
Measure 2
Measure 3
Measure 4
Measure 1
Measure 2
Measure 3
Measure 4
CSF 1
CSF 2
CSF 3
CSF 4
Measure 1
Measure 2
Measure 3
Measure 4
Common questions #4:
How are targets set?
•
Targets for
Measures
...
– … are set based on the
business plan
, given the
required/desired
performance for the
business
– … are compared with
historical
data
– … are set at the start of the
year and
reviewed
regularly
•
It helps to have a part of the
dashboard that
re-forecasts
year end results given actual
performance to date
•
Targets for
People
…
– … are set with regard to
measures they can
influence
— the cascade concept
– … are normally
stretch
targets
— requiring some effort
– … relate to
reward and
appraisal
— they are the
―contract‖ a business has with
its employees
•
Actions
taken to achieve those
targets matter as much as whether
they were achieved or not

Five simple steps to
balanced measurement
1. Agree business objectives
2. Develop a strawman Balanced Scorecard
3. Discuss, debate and check how realistic it
would be to implement
– use it as a starting
point
4. Finalise it
5. Ensure operational systems and processes
can deliver the indicators
• A
thriving
business must address at least:
Can we
continue to
improve and
add value?
Innovation
What must
we excel at?
Quality
How do we
keep our
customers?
Customers
Are we
satisfying
those who
fund us?
Financial
Balanced Business
Scorecard focuses on at
least four main areas
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
BALANCED SCORECARD PROJEKTU pusty dla studentów
Balanced Scorecard synteza wskazniki 2011
Balanced Scorecard demo
Balanced Scorecard, ZARZĄDZANIE, RACHUNKOWOŚĆ, Rachunkowość(3)
Balanced Scorecard, Balanced Scorecard - Strategiczna Karta Wyników
BALANCED SCORECARD PROJEKTU pusty dla studentów
Create a Balanced Scorecard (SharePoint Server 2010)
Balanced Scorecard
IR Lecture1
uml LECTURE
lecture3 complexity introduction
196 Capital structure Intro lecture 1id 18514 ppt
Lecture VIII Morphology
benzen lecture
lecture 1
więcej podobnych podstron
